Experience Tumblr like never before
Space Wallpapers - Blog Posts

Do you believe in magic? ✨ While appearing as a delicate and light veil draped across the sky, this @NASAHubble image reminds us of the power of imagination. What does this look like to you? In reality, it's a small section of a Cygnus supernova blast wave, located around 2,400 light-years away. The original supernova explosion blasted apart a dying star about 20 times more massive than our Sun between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. Since then, the remnant has expanded 60 light-years from its center. Credit: @ESA/Hubble & NASA, W. Blair; acknowledgment: Leo Shatz
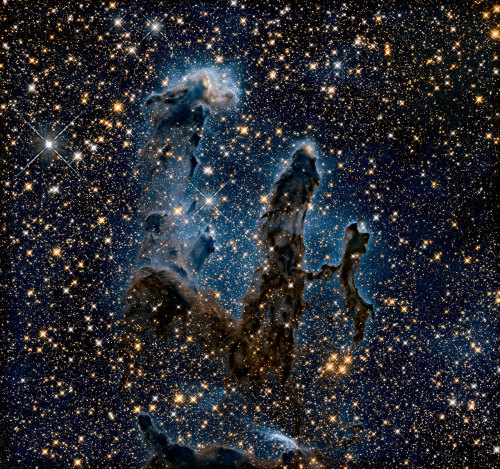
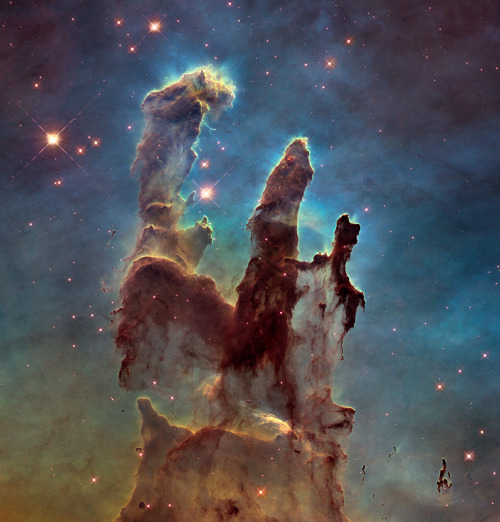


Sometimes... there’s more than meets the eye. 👀 You’re looking at two very different takes on an iconic image.
Human eyes can see only a small portion of the range of radiation given off by the objects around us. We call this wide array of radiation the electromagnetic spectrum, and the part we can see visible light.
In the first image, researchers revisited one of Hubble Space Telescope’s most popular sights: the Eagle Nebula’s Pillars of Creation. Here, the pillars are seen in infrared light, which pierces through obscuring dust and gas and unveil a more unfamiliar — but just as amazing — view of the pillars. The entire frame is peppered with bright stars and baby stars are revealed being formed within the pillars themselves. The image on the bottom is the pillars in visible light.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA/Hubble and the Hubble Heritage Team
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Up for some virtual cloud watching? ☁️
What do you see in Jupiter's hazy atmosphere?
Our NASA JunoCam mission captured this look at the planet’s thunderous northern region during the spacecraft’s close approach to the planet on Feb. 17, 2020.
Some notable features in this view are the long, thin bands that run through the center of the image from top to bottom. Juno has observed these long streaks since its first close pass by Jupiter in 2016.
Image Credits: Image data: NASA / JPL / SwRI / MSSS Image Processing: Citizen Scientist Eichstädt
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

“Only in the darkness can you see the stars.” —Martin Luther King, Jr. Pause for a moment and take in the vastness and beauty of our home planet captured from the vantage point of space. On this spaceship we call Earth, we are all in this together. 💙
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
On Top of The World – Literally
What’s one perk about applying to #BeAnAstronaut? You’re one step closer to being on top of the world.

Part of the job of a NASA astronaut is a task called spacewalking. Spacewalking refers to any time an astronaut gets out of a vehicle while in space; it is performed for many reasons such as completing repairs outside the International Space Station, conducting science experiments and testing new equipment.

Spacewalking can last anywhere from five to eight hours, and for that reason, astronauts’ spacesuits are more like mini-spacecraft than uniforms! Inside spacesuits, astronauts have the oxygen they need to breathe, water to drink and a bathroom!

Spacesuits also protect astronauts from the extreme environment of space. In Earth orbit, conditions can be as cold as minus 250 degrees Fahrenheit. In the sunlight, they can be as hot as 250 degrees. A spacesuit protects astronauts from those extreme temperatures.

To stay safe during spacewalks, astronauts are tethered to the International Space Station. The tethers, like ropes, are hooked to the astronaut and the space station – ensuring the astronaut does not float away into space.

Spacewalking can be a demanding task. Astronauts can burn anywhere from ~1500-2500 calories during one full assignment. That’s about equal to running 2/3 of a marathon.

Does spacewalking sound like something you’d be interested in? If so, you might want to APPLY to #BeAnAstronaut! Applications are open until March 31. Don’t miss your chance to!

Want to learn more about what it takes to be an astronaut? Or, maybe you just want more epic images. Either way, check out nasa.gov/astronauts for all your NASA astronaut needs!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com


In Roman mythology, the god Jupiter drew a veil of clouds around himself to hide his mischief. It was only Jupiter's wife, the goddess Juno, who could peer through the clouds and reveal Jupiter's true nature. Our @NASAJuno spacecraft is looking beneath the clouds of the massive gas giant, not seeking signs of misbehavior, but helping us to understand the planet's structure and history... Now, @NASAJuno just published its first findings on the amount of water in the gas giant’s atmosphere. The Juno results estimate that at the equator, water makes up about 0.25% of the molecules in Jupiter's atmosphere — almost three times that of the Sun. An accurate total estimate of this water is critical to solving the mystery of how our solar system formed.
The JunoCam imager aboard Juno captured this image of Jupiter's southern equatorial region on Sept. 1, 2017. The bottom image is oriented so Jupiter's poles (not visible) run left-to-right of frame.
Image credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill

“We saw to the edge of all there is—
So brutal and alive it seemed to comprehend us back.”
-Tracy K. Smith, US Poet Laureate
Some pictures are worth a thousand words and some a thousand thoughts. On Jan. 31, astronaut Christina Koch shared this emotional view and quote from the International Space Station. Enjoy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Unveiling the Center of Our Milky Way Galaxy

We captured an extremely crisp infrared image of the center of our Milky Way galaxy. Spanning more than 600 light-years, this panorama reveals details within the dense swirls of gas and dust in high resolution, opening the door to future research into how massive stars are forming and what’s feeding the supermassive black hole at our galaxy’s core.

Among the features coming into focus are the jutting curves of the Arches Cluster containing the densest concentration of stars in our galaxy, as well as the Quintuplet Cluster with stars a million times brighter than our Sun. Our galaxy’s black hole takes shape with a glimpse of the fiery-looking ring of gas surrounding it.
The new view was made by the world’s largest airborne telescope, the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy, or SOFIA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Chart-Topping Space Images From 2019 You Won’t Want to Miss
From the first-ever image of a black hole, to astronaut Christina Koch breaking the record for the longest single spaceflight by a woman – 2019 was full of awe-inspiring events!
As we look forward to a new decade, we’ve taken ten of our top Instagram posts and put them here for your viewing pleasure. With eight out of ten being carousels, be sure to click on each title to navigate to the full post.
1. First-Ever Black Hole Image Makes History

In a historic feat by the Event horizon Telescope and National Science Foundation, an image of a black hole and its shadow was captured for the first time. At a whopping 3.4 million likes, this image takes home the gold as our most loved photo of 2019. Several of our missions were part of a large effort to observe this black hole using different wavelengths of light and collect data to understand its environment. Here’s a look at our Chandra X-Ray Observatory’s close-up of the core of the M87 galaxy with the imaged black hole at its center.
2. Hubble Celebrates 29 Years of Dazzling Discoveries


When you wish upon a star… Hubble captures it from afar ✨On April 18, 2019 our Hubble Space Telescope celebrated 29 years of dazzling discoveries, serving as a window to the wonders of worlds light-years away.
Hubble continues to observe the universe in near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light. Over the past 29 years, it has captured the farthest views ever taken of the evolving universe, found planet-forming disks around nearby stars and identified the first supermassive black hole in the heart of a neighboring galaxy. Want more? Enjoy the full 10 photo Instagram carousel here.
3. Stars and Stripes in Space for Flag Day


Patriotism was in the air June 14 for Flag Day, and coming in at number three in our most liked Instagram line up is a carousel of our stars and stripes in space! One of the most iconic images from the Apollo 11 missions is of Buzz Aldrin saluting the American flag on the surface of the Moon. But did you know that over the years, five more flags joined the one left by Apollo 11 – and that many other flags have flown onboard our spacecraft? Scroll through the full carousel for flag day here.
4. Spitzer Celebrates its Super Sweet 16!


Since 2003, our Spitzer Space Telescope has been lifting the veil on the wonders of the cosmos, from our own solar system to faraway galaxies, using infrared light! Thanks to Spitzer, we've confirm the presence of seven rocky, Earth-size planets, received weather maps of hot, gaseous exoplanets and discovered a hidden ring around Saturn. In honor of Spitzer's Sweet 16 in space, enjoy 16 jaw-dropping images from its mission here.
5. Earth as Seen Through Our Astronauts’ Eyes Show Perspective Changing Views

“That's here. That's home. That's us.” – Carl Sagan
Seeing Earth from space can alter an astronauts’ cosmic perspective, a mental shift known as the “Overview Effect.” First coined by space writer Frank White in 1987, the Overview Effect is described as a feeling of awe for our home planet and a sense of responsibility for taking care of it. See Earth from the vantage point of our astronauts in a carousel of perspective-changing views here.
6. Astronaut Christina Koch Breaks Record for Longest Single Spaceflight by Woman


Astronaut Christina Koch (@Astro_Christina) set a record Dec. 28, 2019 for the longest single spaceflight by a woman, eclipsing the former record of 288 days set by Peggy Whitson. Her long-duration mission is helping us learn how to keep astronauts healthy for deep space exploration to the Moon and Mars. Congrats to Christina on reaching new heights! Join in the celebration and view few photos she captured from her vantage point aboard the Space Station here.
7. Our Beautiful Planet – The Only Place We Know to Harbor Life – From Space


Earth is special. It’s the only place in the universe that we know contains life.
On July 7, 2019, two million people joined us in celebrating its beauty with a jaw dropping carousel of our home planet, as captured by crew members aboard the International Space Station. Bright blue oceans, glowing city lights and ice-capped mountain peaks come to life in a collection of breathtaking images, found here.
8. A Moon Even Sinatra Couldn’t Help But Sing About

Every 29 days our Moon turns over a new leaf, and on May, 18 we saw a very special one of its faces. Appearing opposite the Sun at 5:11 p.m. EDT, the world looked up to find a Blue Moon! Though the Moon didn’t actually look blue, the site of one is kind of rare. They occur on average about every two-and-a-half years when a season ends up having four full moons instead of three. Click through a carousel of high-definition lunar phases here.
9. The Majesty of Hubble Imagery ... From Your Backyard


On December 23, a new gallery of Hubble Space Telescope images highlighting celestial objects visible to amateur and professional astronomers alike was released. All of the objects are from a collection known as the Caldwell catalog, which includes 109 interesting objects visible in amateur-sized telescopes in both the northern and southern skies. Flip through the jaw-dropping carousel here, and learn more about how you can study the night sky with Hubble here.
10. The Moon Gets Sassy

Nobody:
The Moon: “Y'all on the way yet?” 👀
We're working on it, Moon. Under the Artemis program, we're sending the first woman and the next man to walk on your surface by 2024. Find out how we’re doing it here.

For more pictures like these, follow us on Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/nasa/
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com






Be your own explorer ✨the cosmos is waiting...
From nearby clouds of gas and dust to remote galaxies that formed billions of years ago, tour the night sky with our Hubble Space Telescope’s new Caldwell catalog. The catalog of star clusters, galaxies and nebulas was first produced to highlight cosmic wonders visible to amateur astronomers. Since then Hubble has taken images of 95 out of the 109 objects, bringing these objects to life in exquisite detail.
While the objects can be observed using modest ground-based telescopes, Hubble’s Caldwell collection has been assembled for astronomers to see the finer details of each object in the night sky.
View the full collection here!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
The Overview Effect
Observing Earth from space can alter an astronauts’ cosmic perspective, a mental shift known as the “Overview Effect.” First coined by space writer Frank White in 1987, the Overview Effect is described as a feeling of awe for our home planet and a sense of responsibility for taking care of it.
See Earth from the vantage point of our astronauts in these perspective-changing views:
Floating Free in Space

Astronaut Bruce McCandless II used his hands to control his movement above the Earth during the first-ever spacewalk that didn't use restrictive tethers and umbilicals. Fellow crew members aboard the space shuttle Challenger captured this image on Feb. 7, 1984, through windows on the flight deck.
Of his famous spacewalk, McCandless wrote in 2015: "My wife [Bernice] was at mission control, and there was quite a bit of apprehension. I wanted to say something similar to Neil [Armstrong] when he landed on the moon, so I said, 'It may have been a small step for Neil, but it’s a heck of a big leap for me.' That loosened the tension a bit."
Earth Reflections

Astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson looks through a window in the Cupola of the International Space Station (ISS). A blue and white part of Earth and the blackness of space are visible through the windows. The image was a self-portrait using natural light.
In a preflight interview for Expedition 23/24, Dyson said: “hands down, the best part about it is being able to look at that view every day and during the time frame we’ll be up there, hopefully, we’ll have a big bay window and much more opportunity to observe this beautiful planet.”
Taking in the View

As astronaut Nick Hague prepared to conclude his six-month stay aboard the ISS, he shared this photo saying: "Today is my last Monday living on this orbiting laboratory and I’m soaking up my final views. The @Space_Station is truly an engineering marvel. #MondayMotivation."
He and Expedition 60 and Soyuz commander Alexey Ovchinin of the Russian space agency Roscosmos completed a 203-day mission, spanning 3,248 orbits of Earth, and a journey of 80.8 million miles.
Earthrise

On Dec. 24, 1968, Apollo 8 astronauts Frank Borman, Jim Lovell and Bill Anders became the first humans to witness the Earth rising above the Moon's surface.
Anders, photographing the Moon from the right-side window, caught sight of the view, and exclaimed: “Oh my God, look at that picture over there! There’s the Earth comin’ up. Wow, is that pretty!”
The Blue Marble

Besides Earthrise, the Blue Marble is probably the most famous image of Earth that NASA has produced. Taken by the Apollo 17 crew on their way to the Moon in 1972, the Blue Marble and other NASA imagery of Earth has been credited by some with helping to fuel the environmental movement.
For more information on the Overview Effect, check out this episode of Houston We Have a Podcast.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Say hello to the Saturn Nebula 👋
Garden-variety stars like the Sun live fairly placid lives in their galactic neighborhoods, casually churning out heat and light for billions of years. When these stars reach retirement age, however, they transform into unique and often psychedelic works of art. This Hubble Space Telescope image of the Saturn Nebula shows the result, called a planetary nebula. While it looks like a piece of wrapped cosmic candy, what we see is actually the outer layers of a dying star.
Stars are powered by nuclear fusion, but each one comes with a limited supply of fuel. When a medium-mass star exhausts its nuclear fuel, it will swell up and shrug off its outer layers until only a small, hot core remains. The leftover core, called a white dwarf, is a lot like a hot coal that glows after a barbecue — eventually it will fade out. Until then, the gaseous debris fluoresces as it expands out into the cosmos, possibly destined to be recycled into later generations of stars and planets.
Using Hubble’s observations, scientists have characterized the nebula’s composition, structure, temperature and the way it interacts with surrounding material. Studying planetary nebulas is particularly interesting since our Sun will experience a similar fate around five billion years down the road.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

We are swooningggg over this NEW Saturn image.
Saturn is so beautiful that astronomers cannot resist using the Hubble Space Telescope to take yearly snapshots of the ringed world when it is at its closest distance to Earth. 😍
These images, however, are more than just beauty shots. They reveal exquisite details of the planet as a part of the Outer Planets Atmospheres Legacy project to help scientists understand the atmospheric dynamics of our solar system's gas giants.
This year's Hubble offering, for example, shows that a large storm visible in the 2018 Hubble image in the north polar region has vanished. Also, the mysterious six-sided pattern – called the "hexagon" – still exists on the north pole. Caused by a high-speed jet stream, the hexagon was first discovered in 1981 by our Voyager 1 spacecraft.
Saturn's signature rings are still as stunning as ever. The image reveals that the ring system is tilted toward Earth, giving viewers a magnificent look at the bright, icy structure.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, A. Simon (GSFC), M.H. Wong (University of California, Berkeley) and the OPAL Team
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
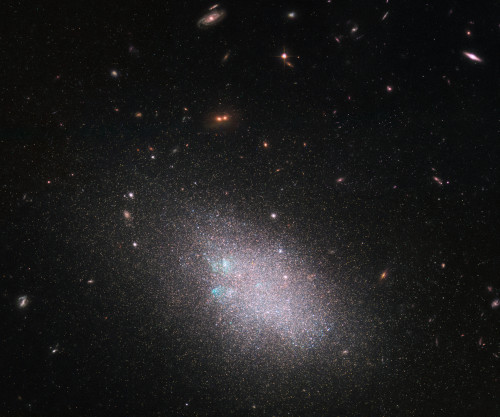

Look! A cosmic block party 🥳 In this Hubble image, you’ll find 50 spiral and dwarf galaxies hanging out in our cosmic neighborhood. The main focal point of stars is actually a dwarf galaxy. Dwarf galaxies often show a hazy structure, an ill-defined shape and an appearance somewhat akin to a swarm or cloud of stars — and UGC 685 is no exception to this. These data were gathered under Hubble’s Legacy ExtraGalactic UV Survey (LEGUS) program, the sharpest and most comprehensive ultraviolet survey of star-forming galaxies in the nearby universe. Image Credit: ESA/Hubble & NASA; the LEGUS team, B. Tully, D. Calzetti
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Sixteen Images for Spitzer's Sweet 16! 🎂
We launched our Spitzer Space Telescope into orbit around the Sunday on Aug. 25, 2003. Since then, the observatory has been lifting the veil on the wonders of the cosmos, from our own solar system to faraway galaxies, using infrared light.
Thanks to Spitzer, scientists were able to confirm the presence of seven rocky, Earth-size planets in the TRAPPIST-1 system. The telescope has also provided weather maps of hot, gaseous exoplanets and revealed a hidden ring around Saturn. It has illuminated hidden collections of dust in a wide variety of locations, including cosmic nebulas (clouds of gas and dust in space), where young stars form, and swirling galaxies. Spitzer has additionally investigated some of the universe's oldest galaxies and stared at the black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
In honor of Spitzer's Sweet 16 in space, here are 16 amazing images from the mission.
Giant Star Makes Waves

This Spitzer image shows the giant star Zeta Ophiuchi and the bow shock, or shock wave, in front of it. Visible only in infrared light, the bow shock is created by winds that flow from the star, making ripples in the surrounding dust.
The Seven Sisters Pose for Spitzer

The Pleiades star cluster, also known as the Seven Sisters, is a frequent target for night sky observers. This image from Spitzer zooms in on a few members of the sisterhood. The filaments surrounding the stars are dust, and the three colors represent different wavelengths of infrared light.
Young Stars in Their Baby Blanket of Dust

Newborn stars peek out from beneath their blanket of dust in this image of the Rho Ophiuchi nebula. Called "Rho Oph" by astronomers and located about 400 light-years from Earth, it's one of the closest star-forming regions to our own solar system.
The youngest stars in this image are surrounded by dusty disks of material from which the stars — and their potential planetary systems — are forming. More evolved stars, which have shed their natal material, are blue.
The Infrared Helix

Located about 700 light-years from Earth, the eye-like Helix nebula is a planetary nebula, or the remains of a Sun-like star. When these stars run out of their internal fuel supply, their outer layers puff up to create the nebula. Our Sun will blossom into a planetary nebula when it dies in about 5 billion years.
The Tortured Clouds of Eta Carinae

The bright star at the center of this image is Eta Carinae, one of the most massive stars in the Milky Way galaxy. With around 100 times the mass of the Sun and at least 1 million times the brightness, Eta Carinae releases a tremendous outflow of energy that has eroded the surrounding nebula.
Spitzer Spies Spectacular Sombrero

Located 28 million light-years from Earth, Messier 104 — also called the Sombrero galaxy or M104 — is notable for its nearly edge-on orientation as seen from our planet. Spitzer observations were the first to reveal the smooth, bright ring of dust (seen in red) circling the galaxy.
Spiral Galaxy Messier 81

This infrared image of the galaxy Messier 81, or M81, reveals lanes of dust illuminated by active star formation throughout the galaxy's spiral arms. Located in the northern constellation of Ursa Major (which includes the Big Dipper), M81 is also about 12 million light-years from Earth.
Spitzer Reveals Stellar Smoke

Messier 82 — also known as the Cigar galaxy or M82 — is a hotbed of young, massive stars. In visible light, it appears as a diffuse bar of blue light, but in this infrared image, scientists can see huge red clouds of dust blown out into space by winds and radiation from those stars.
A Pinwheel Galaxy Rainbow

This image of Messier 101, also known as the Pinwheel Galaxy or M101, combines data in the infrared, visible, ultraviolet and X-rays from Spitzer and three other NASA space telescopes: Hubble, the Galaxy Evolution Explorer's Far Ultraviolet detector (GALEX) and the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. The galaxy is about 70% larger than our own Milky Way, with a diameter of about 170,000 light-years, and sits at a distance of 21 million light-years from Earth. Read more about its colors here.
Cartwheel Galaxy Makes Waves

Approximately 100 million years ago, a smaller galaxy plunged through the heart of the Cartwheel galaxy, creating ripples of brief star formation. As with the Pinwheel galaxy above, this composite image includes data from NASA's Spitzer, Hubble, GALEX and Chandra observatories.
The first ripple appears as a bright blue outer ring around the larger object, radiating ultraviolet light visible to GALEX. The clumps of pink along the outer blue ring are X-ray (observed by Chandra) and ultraviolet radiation.
Spitzer and Hubble Create Colorful Masterpiece

Located 1,500 light-years from Earth, the Orion nebula is the brightest spot in the sword of the constellation Orion. Four massive stars, collectively called the Trapezium, appear as a yellow smudge near the image center. Visible and ultraviolet data from Hubble appear as swirls of green that indicate the presence of gas heated by intense ultraviolet radiation from the Trapezium's stars. Less-embedded stars appear as specks of green, and foreground stars as blue spots. Meanwhile, Spitzer's infrared view exposes carbon-rich molecules called polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, shown here as wisps of red and orange. Orange-yellow dots are infant stars deeply embedded in cocoons of dust and gas.
A Space Spider Watches Over Young Stars

Located about 10,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Auriga, the Spider nebula resides in the outer part of the Milky Way. Combining data from Spitzer and the Two Micron All Sky Survey (2MASS), the image shows green clouds of dust illuminated by star formation in the region.
North America Nebula in Different Lights

This view of the North America nebula combines visible light collected by the Digitized Sky Survey with infrared light from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. Blue hues represent visible light, while infrared is displayed as red and green. Clusters of young stars (about 1 million years old) can be found throughout the image.
Spitzer Captures Our Galaxy's Bustling Center

This infrared mosaic offers a stunning view of the Milky Way galaxy's busy center. The pictured region, located in the Sagittarius constellation, is 900 light-years agross and shows hundreds of thousands of mostly old stars amid clouds of glowing dust lit up by younger, more massive stars. Our Sun is located 26,000 light-years away in a more peaceful, spacious neighborhood, out in the galactic suburbs.
The Eternal Life of Stardust

The Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy located about 160,000 light-years from Earth, looks like a choppy sea of dust in this infrared portrait. The blue color, seen most prominently in the central bar, represents starlight from older stars. The chaotic, bright regions outside this bar are filled with hot, massive stars buried in thick blankets of dust.
A Stellar Family Portrait

In this large celestial mosaic from Spitzer, there's a lot to see, including multiple clusters of stars born from the same dense clumps of gas and dust. The grand green-and-orange delta filling most of the image is a faraway nebula. The bright white region at its tip is illuminated by massive stars, and dust that has been heated by the stars' radiation creates the surrounding red glow.
Managed by our Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, Spitzer's primary mission lasted five-and-a-half years and ended when it ran out of the liquid helium coolant necessary to operate two of its three instruments. But, its passive-cooling design has allowed part of its third instrument to continue operating for more than 10 additional years. The mission is scheduled to end on Jan. 30, 2020.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

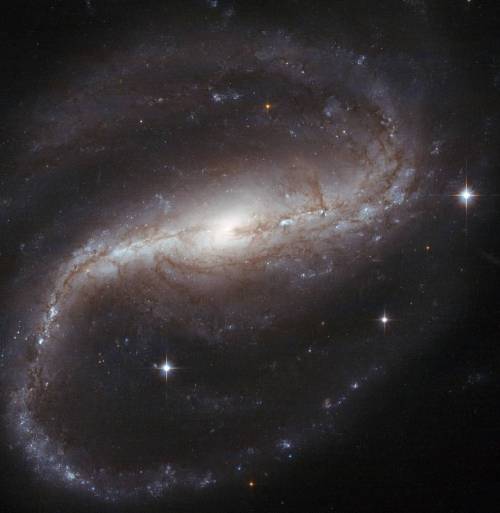
Say hello to spiral galaxy NGC 1097 👋
About 45 million light-years away, in another corner of the cosmos, lies spiral galaxy NGC 1097. Though this Hubble Space Telescope image zooms in toward the core, the galaxy’s vast spiral arms span over 100,000 light-years as they silently sweep through space. At the heart of this galaxy lurks a black hole that is about 100 million times as massive as the Sun.
The supermassive black hole is voraciously eating up surrounding matter, which forms a doughnut-shaped ring around it. Matter that's pulled into the black hole releases powerful radiation, making the star-filled center of the galaxy even brighter. Hubble’s observations have led to the discovery that while the material that is drawn toward NGC 1097’s black hole may be doomed to die, new stars are bursting into life in the ring around it.
This sparkling spiral galaxy is especially interesting to both professional scientists and amateur astronomers. It is a popular target for supernova hunters ever since the galaxy experienced three supernovas in relatively rapid succession — just over a decade, between 1992 and 2003. Scientists are intrigued by the galaxy’s satellites — smaller “dwarf” galaxies that orbit NGC 1097 like moons. Studying this set of galaxies could reveal new information about how galaxies interact with each other and co-evolve.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
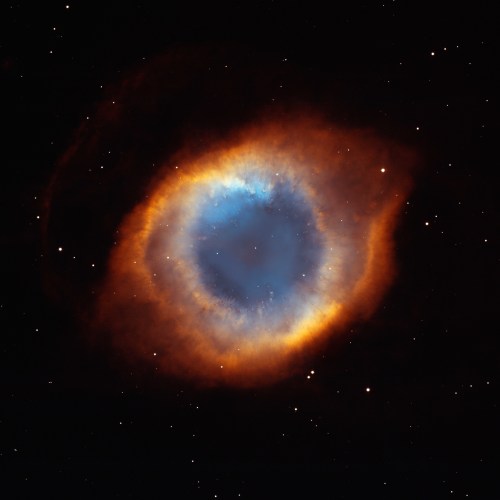
Say hello to the Helix Nebula 👋
In 2001 and 2002, our Hubble Space Telescope looked at the Helix Nebula and it looked right back! This planetary nebula is right in our cosmic neighborhood, only about 650 light-years away. Gigantic for this type of cosmic object, the Helix Nebula stretches across 2 to 3 light-years.
With no actual connection to planets, planetary nebulas like this one are produced when a medium-mass star dies and sloughs off its outer layers. These gaseous layers are expelled into space at astonishing speeds where they light up like fireworks. The Helix Nebula is one of the closest planetary nebulas to Earth, giving scientists an up-close view of its strange affairs.
Through Hubble’s observations, scientists have learned that the Helix Nebula isn’t doughnut-shaped as it appears. Instead it consists of two disks that are nearly perpendicular to each other — the nebula looks like an eye and bulges out like one too!
Hubble has also imaged comet-like tendrils that form a pattern around the central star like the spokes on a wagon wheel, likely resulting from a collision between gases. The dying star spews hot gas from its surface, which crashes into the cooler gas that it ejected 10,000 years before. Eventually the knots will dissipate into the cold blackness of interstellar space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

No, this red beam in space isn't a light saber! It's a galaxy, far, far away — 44 million light-years away, to be exact.
We often imagine galaxies as having massive spiral arms or thick disks of dust, but not all galaxies are oriented face-on as viewed from Earth. From our viewpoint, our Spitzer Space Telescope can detect this galaxy's infrared light but can only view the entire galaxy on its side where we can't see its spiral features. We know it has a diameter of roughly 60,000 light-years — a little more than half the diameter of our own Milky Way galaxy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.


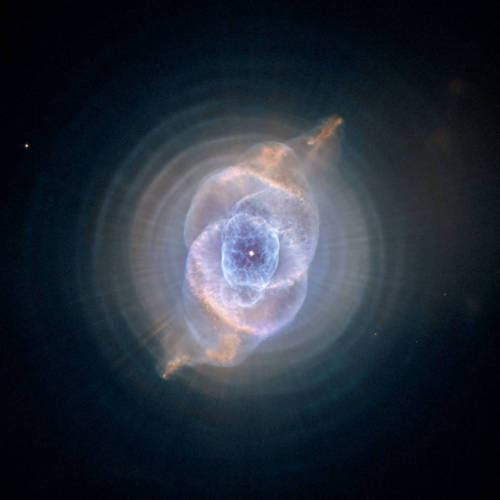
#InternationalCatDay? Try #IntergalacticCatDay.
Check out features of our feline friends that have come to life as interstellar phenomena!
Pictured first, the Cat’s Paw Nebula is located about 4,200-5,500 light-years from Earth – situated in our very own Milky Way Galaxy. It was named for the large, round features that create the impression of a feline footprint and was captured by our Spitzer Space Telescope. After gas and dust inside the nebula collapse to form stars, the stars may in turn heat up the pressurized gas surrounding them. This process causes the gas to expand into space and form the bright red bubbles you see. The green areas show places where radiation from hot stars collided with large molecules called "polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons," causing them to fluoresce.
Next, you’ll find the Cat’s Eye Nebula. Residing 3,000 light-years from Earth, the Cat’s Eye represents a brief, yet glorious, phase in the life of a sun-like star. This nebula's dying central star may have produced the simple, outer pattern of dusty concentric shells by shrugging off outer layers in a series of regular convulsions. To create this view, Hubble Space Telescope archival image data have been reprocessed. Compared to well-known Hubble pictures, the alternative processing strives to sharpen and improve the visibility of details in light and dark areas of the nebula and also applies a more complex color palette. Gazing into the Cat's Eye, astronomers may well be seeing the fate of our sun, destined to enter its own planetary nebula phase of evolution ... in about 5 billion years.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Say hello to the Jewel Box Cluster 👋
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a young, open star cluster known as NGC 4755 or the Jewel Box. Just like old school friends that drift apart after graduation, the stars in open clusters only remain together for a limited time. They disperse into space over the course of a few hundred million years, pulled away by the gravitational tugs of other passing clusters and clouds of gas.
The Jewel Box is a spartan collection of just over 100 stars. The cluster is about 6,500 light-years away from Earth, which means that the light we see from it today was emitted before the Great Pyramids in Egypt were built.
Head outside and you can see it for yourself! The Jewel Box is visible to the naked eye, but will masquerade as a single star. Grab a pair of binoculars if you want to see more of the cluster’s sparkling stellar population. It is located in the southern constellation of the cross (Crux).
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Say hello to the Carina Nebula 👋
One of the largest panoramic images ever taken with our Hubble Space Telescope’s cameras, this image features a stunning 50-light-year-wide view of the intense central region of the Carina Nebula - a strange stellar nursery. The nebula is sculpted by the action of outflowing winds and scorching ultraviolet radiation from the monster stars that inhabit this inferno. The Carina Nebula lies within our own galaxy, about 7,500 light-years away.
At the heart of the nebula is Eta Carinae — a system of two stars. The larger star, Eta Car A, is around 100 times as massive as the Sun and 5 million times as luminous! Stars of this size are extremely rare; our galaxy is home to hundreds of billions of stars, but only tens of them are as massive as Eta Car A.
This view of the Carina Nebula provided astronomers the opportunity to explore the process of star birth at a new level of detail. The hurricane-strength blast of stellar winds and blistering ultraviolet radiation within the cavity are now compressing the surrounding walls of cold hydrogen. This is triggering a second stage of new star formation. Hubble has also enabled scientists to generate 3-D models that reveal never-before-seen features of the interactions between the Eta Carinae star system.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Say hello to spiral galaxy NGC 7331👋
Happy National Twin Day!
The majestic spiral galaxy NGC 7331 is almost like a long lost twin to our very own Milky Way. In this close-up, the galaxy’s magnificent spiral arms feature dark, obscuring dust lanes, bright bluish clusters of massive young stars and the telltale reddish glow of active star-forming regions. The yellowish central region harbors populations of older, cooler stars. Like in the Milky Way, a supermassive black hole lies at the galaxy’s core.
Our Hubble Space Telescope took this image while observing a supernova explosion — the fiery death of a massive star — within NGC 7331. Astronomers noted that the supernova, called SN 2014C, experienced a dramatic, hasty transformation that involved a significant upsurge in hydrogen content. This observation provided a rare chance to gain insight into the final stages of massive stars.
NGC 7331 was discovered in 1784 by famed astronomer William Herschel, who discovered the planet Uranus. It was originally classified as a nebula, which is an interstellar cloud of gas and dust, because no one knew that other galaxies existed until the 20th century. It turns out that NGC 7331 and the Milky Way are among billions and billions of galaxies in the universe!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Say hello to globular cluster 47 Tucanae 👋
This glittery spray of ancient stars is about 16,700 light-years away from Earth toward the constellation Tucana. Globular clusters like this one are isolated star cities, home to hundreds of thousands of stars that are held together by their mutual gravity. And like the fast pace of cities, there's plenty of action in these stellar metropolises. The stars are in constant motion, orbiting around the cluster's center.
Past observations have shown that the heavyweight stars tend to crowd into the “downtown” core area, while lightweight stars reside in the less populated suburbs. But as heavyweight stars age, they rapidly lose mass, cool down and shut off their nuclear furnaces. After the purge, only the stars' bright, superhot cores – called white dwarfs – remain. This weight loss program causes the now lighter-weight white dwarfs to be nudged out of the downtown area through gravitational interactions with heftier stars.
Until these Hubble observations, astronomers had never seen the dynamic conveyor belt in action. The Hubble results reveal young white dwarfs amid their leisurely 40-million-year exodus from the bustling center of the cluster.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

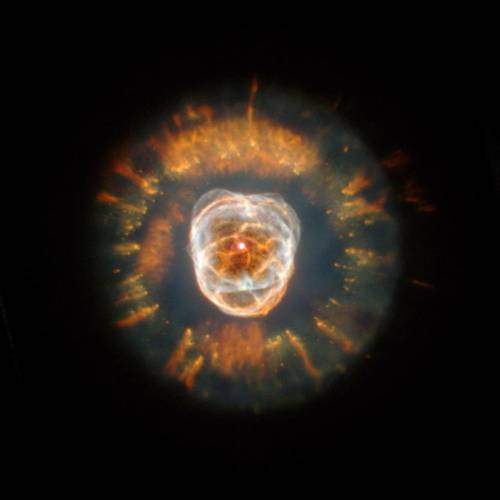
Say hello to the Eskimo Nebula 👋
This nebula began forming about 10,000 years ago when a dying star started flinging material into space. When Sun-like stars exhaust their nuclear fuel, they become unstable and blast their outer layers of gas away into space (bad news for any planets in the area). This Hubble Space Telescope image shows a snapshot of the unworldly process.
Streams of high-energy ultraviolet radiation cause the expelled material to glow, creating a beautiful planetary nebula — a term chosen for the similarity in appearance to the round disk of a planet when viewed through a small telescope.
The Eskimo Nebula got its nickname because it resembles a face surrounded by a fur parka. The “parka” is a disk of material embellished by a ring of comet-shaped objects with their tails streaming away from the central, dying star. In the middle of the nebula is a bubble of material that is being blown outward by the star’s intense “wind” of high-speed material.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
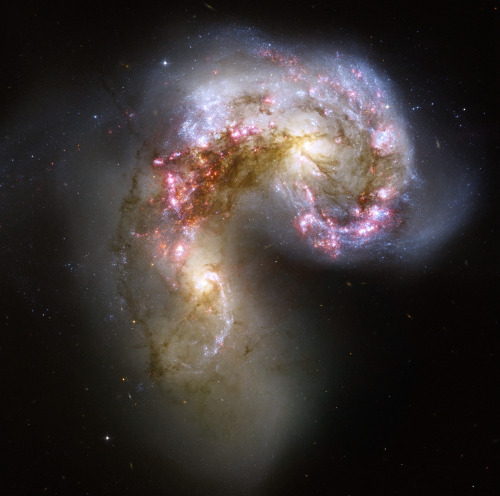

Say hello to the Antennae galaxies 👋
Two galaxies are locked in a deadly embrace in this Hubble Space Telescope image. Once normal, sedate spiral galaxies like the Milky Way, this galactic pair has spent the past few hundred million years sparring. The clash is so violent that stars have been ripped from their host galaxies to form a streaming arc between the two.
The far-flung stars and streamers of gas stretch out into space, creating long tidal tails reminiscent of antennae (not visible in this close-up Hubble view). Clouds of gas blossom out in bright pink and red, surrounding the bright flashes of blue star-forming regions — some of which are partially obscured by dark patches of dust.
Hubble’s observations have uncovered over 1,000 bright, young star clusters bursting to life as a result of the head-on wreck. The sweeping spiral-like patterns, traced by bright blue star clusters, shows the result of a firestorm of star-birth activity, which was triggered by the collision. The rate of star formation is so high that the Antennae galaxies are said to be in a state of starburst, a period in which all of the gas within the galaxies is being used to form stars. This cannot last forever, and neither can the separate galaxies; eventually the nuclei will coalesce and the galaxies will begin their retirement together as one large elliptical galaxy.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.

Do you believe in magic? ✨ While appearing as a delicate and light veil draped across the sky, this @NASAHubble image reminds us of the power of imagination. What does this look like to you? In reality, it’s a small section of a Cygnus supernova blast wave, located around 2,400 light-years away. The original supernova explosion blasted apart a dying star about 20 times more massive than our Sun between 10,000 and 20,000 years ago. Since then, the remnant has expanded 60 light-years from its center. Credit: @ESA/Hubble & NASA, W. Blair; acknowledgment: Leo Shatz