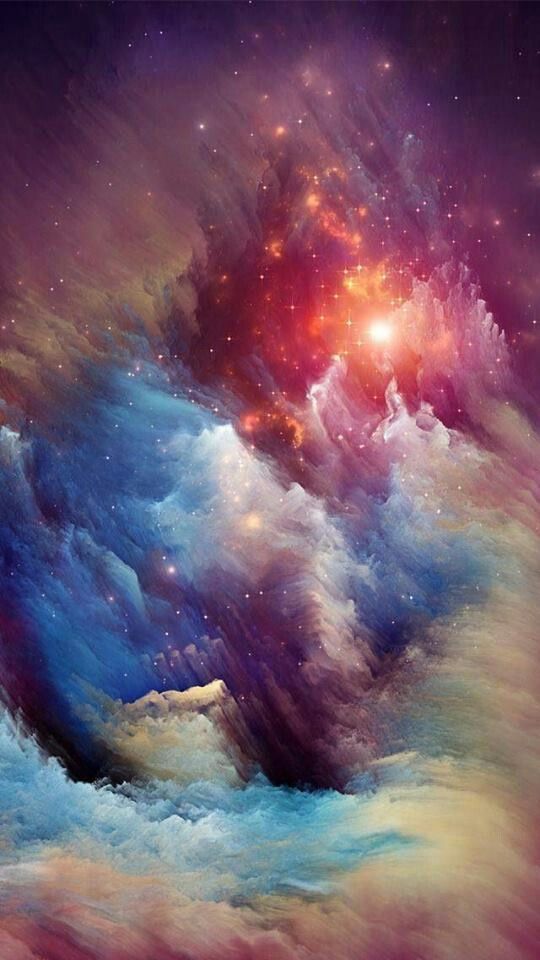
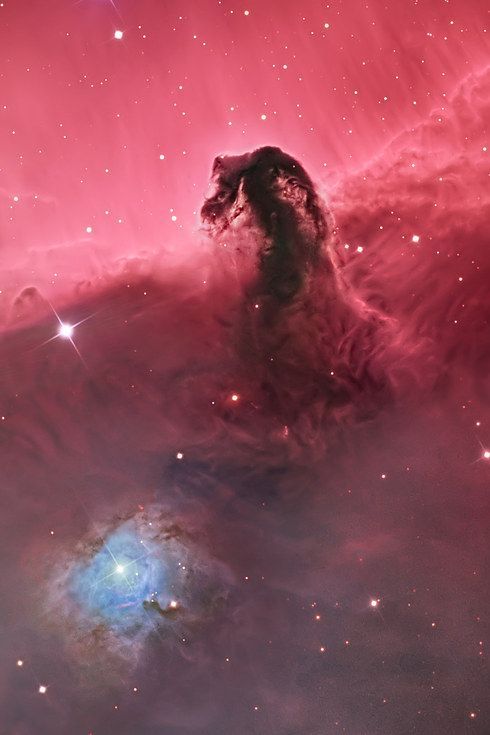
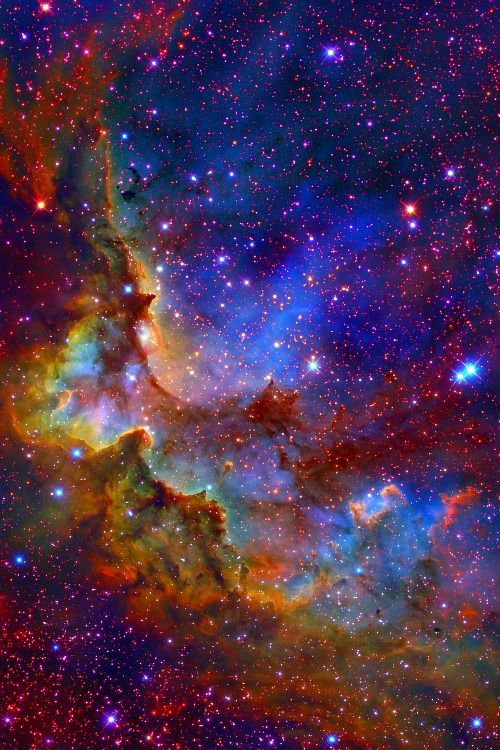
Experience Tumblr like never before
Nebulas - Blog Posts
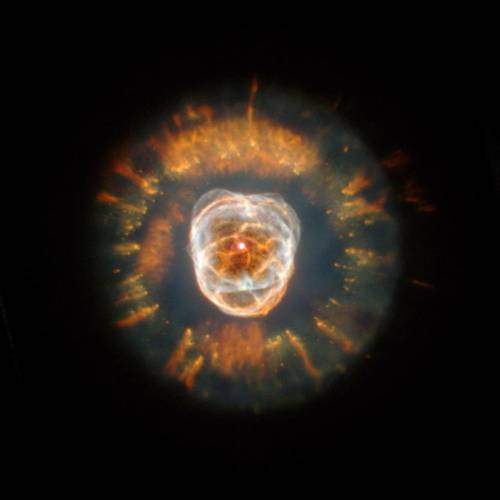
Decoding Nebulae
We can agree that nebulae are some of the most majestic-looking objects in the universe. But what are they exactly? Nebulae are giant clouds of gas and dust in space. They’re commonly associated with two parts of the life cycle of stars: First, they can be nurseries forming new baby stars. Second, expanding clouds of gas and dust can mark where stars have died.

Not all nebulae are alike, and their different appearances tell us what's happening around them. Since not all nebulae emit light of their own, there are different ways that the clouds of gas and dust reveal themselves. Some nebulae scatter the light of stars hiding in or near them. These are called reflection nebulae and are a bit like seeing a street lamp illuminate the fog around it.

In another type, called emission nebulae, stars heat up the clouds of gas, whose chemicals respond by glowing in different colors. Think of it like a neon sign hanging in a shop window!

Finally there are nebulae with dust so thick that we’re unable to see the visible light from young stars shine through it. These are called dark nebulae.

Our missions help us see nebulae and identify the different elements that oftentimes light them up.
The Hubble Space Telescope is able to observe the cosmos in multiple wavelengths of light, ranging from ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared. Hubble peered at the iconic Eagle Nebula in visible and infrared light, revealing these grand spires of dust and countless stars within and around them.

The Chandra X-ray Observatory studies the universe in X-ray light! The spacecraft is helping scientists see features within nebulae that might otherwise be hidden by gas and dust when viewed in longer wavelengths like visible and infrared light. In the Crab Nebula, Chandra sees high-energy X-rays from a pulsar (a type of rapidly spinning neutron star, which is the crushed, city-sized core of a star that exploded as a supernova).

The James Webb Space Telescope will primarily observe the infrared universe. With Webb, scientists will peer deep into clouds of dust and gas to study how stars and planetary systems form.

The Spitzer Space Telescope studied the cosmos for over 16 years before retiring in 2020. With the help of its detectors, Spitzer revealed unknown materials hiding in nebulae — like oddly-shaped molecules and soot-like materials, which were found in the California Nebula.

Studying nebulae helps scientists understand the life cycle of stars. Did you know our Sun got its start in a stellar nursery? Over 4.5 billion years ago, some gas and dust in a nebula clumped together due to gravity, and a baby Sun was born. The process to form a baby star itself can take a million years or more!

After billions more years, our Sun will eventually puff into a huge red giant star before leaving behind a beautiful planetary nebula (so-called because astronomers looking through early telescopes thought they resembled planets), along with a small, dense object called a white dwarf that will cool down very slowly. In fact, we don’t think the universe is old enough yet for any white dwarfs to have cooled down completely.
Since the Sun will live so much longer than us, scientists can't observe its whole life cycle directly ... but they can study tons of other stars and nebulae at different phases of their lives and draw conclusions about where our Sun came from and where it's headed. While studying nebulae, we’re seeing the past, present, and future of our Sun and trillions of others like it in the cosmos.

To keep up with the most recent cosmic news, follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space.
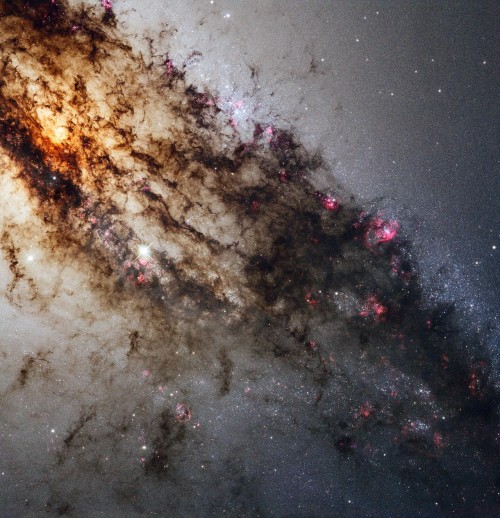
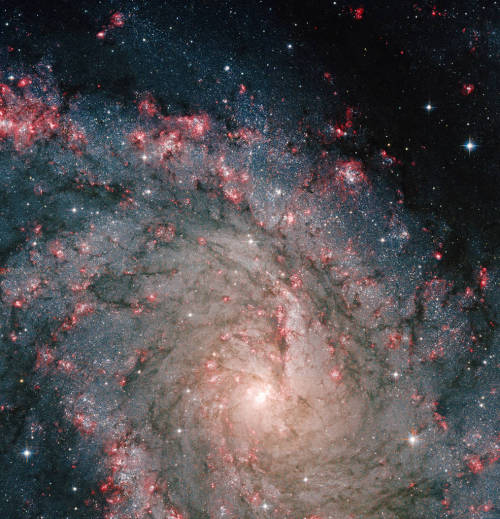
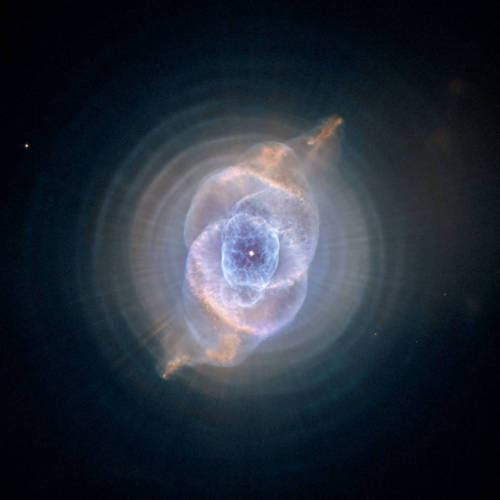
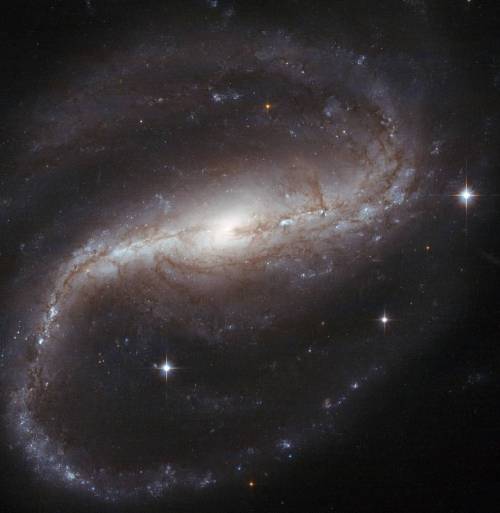
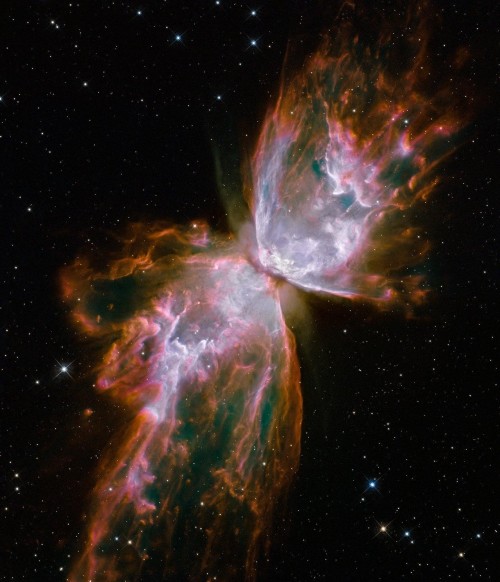






Be your own explorer ✨the cosmos is waiting...
From nearby clouds of gas and dust to remote galaxies that formed billions of years ago, tour the night sky with our Hubble Space Telescope’s new Caldwell catalog. The catalog of star clusters, galaxies and nebulas was first produced to highlight cosmic wonders visible to amateur astronomers. Since then Hubble has taken images of 95 out of the 109 objects, bringing these objects to life in exquisite detail.
While the objects can be observed using modest ground-based telescopes, Hubble’s Caldwell collection has been assembled for astronomers to see the finer details of each object in the night sky.
View the full collection here!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Decoding Nebulae
We can agree that nebulae are some of the most majestic-looking objects in the universe. But what are they exactly? Nebulae are giant clouds of gas and dust in space. They’re commonly associated with two parts of the life cycle of stars: First, they can be nurseries forming new baby stars. Second, expanding clouds of gas and dust can mark where stars have died.

Not all nebulae are alike, and their different appearances tell us what's happening around them. Since not all nebulae emit light of their own, there are different ways that the clouds of gas and dust reveal themselves. Some nebulae scatter the light of stars hiding in or near them. These are called reflection nebulae and are a bit like seeing a street lamp illuminate the fog around it.

In another type, called emission nebulae, stars heat up the clouds of gas, whose chemicals respond by glowing in different colors. Think of it like a neon sign hanging in a shop window!

Finally there are nebulae with dust so thick that we’re unable to see the visible light from young stars shine through it. These are called dark nebulae.

Our missions help us see nebulae and identify the different elements that oftentimes light them up.
The Hubble Space Telescope is able to observe the cosmos in multiple wavelengths of light, ranging from ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared. Hubble peered at the iconic Eagle Nebula in visible and infrared light, revealing these grand spires of dust and countless stars within and around them.

The Chandra X-ray Observatory studies the universe in X-ray light! The spacecraft is helping scientists see features within nebulae that might otherwise be hidden by gas and dust when viewed in longer wavelengths like visible and infrared light. In the Crab Nebula, Chandra sees high-energy X-rays from a pulsar (a type of rapidly spinning neutron star, which is the crushed, city-sized core of a star that exploded as a supernova).

The James Webb Space Telescope will primarily observe the infrared universe. With Webb, scientists will peer deep into clouds of dust and gas to study how stars and planetary systems form.

The Spitzer Space Telescope studied the cosmos for over 16 years before retiring in 2020. With the help of its detectors, Spitzer revealed unknown materials hiding in nebulae — like oddly-shaped molecules and soot-like materials, which were found in the California Nebula.

Studying nebulae helps scientists understand the life cycle of stars. Did you know our Sun got its start in a stellar nursery? Over 4.5 billion years ago, some gas and dust in a nebula clumped together due to gravity, and a baby Sun was born. The process to form a baby star itself can take a million years or more!

After billions more years, our Sun will eventually puff into a huge red giant star before leaving behind a beautiful planetary nebula (so-called because astronomers looking through early telescopes thought they resembled planets), along with a small, dense object called a white dwarf that will cool down very slowly. In fact, we don’t think the universe is old enough yet for any white dwarfs to have cooled down completely.
Since the Sun will live so much longer than us, scientists can't observe its whole life cycle directly ... but they can study tons of other stars and nebulae at different phases of their lives and draw conclusions about where our Sun came from and where it's headed. While studying nebulae, we’re seeing the past, present, and future of our Sun and trillions of others like it in the cosmos.

To keep up with the most recent cosmic news, follow NASA Universe on Twitter and Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space.
#beautiful


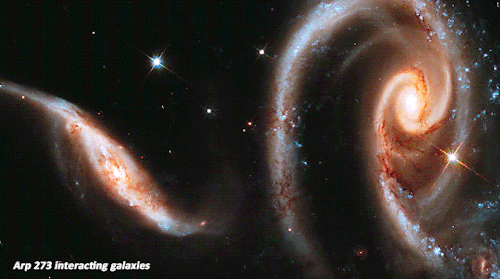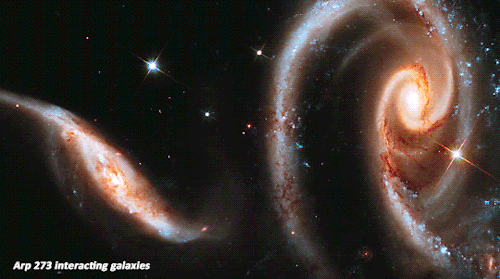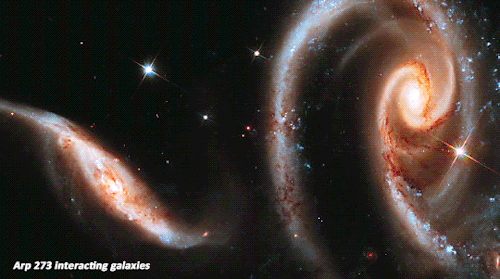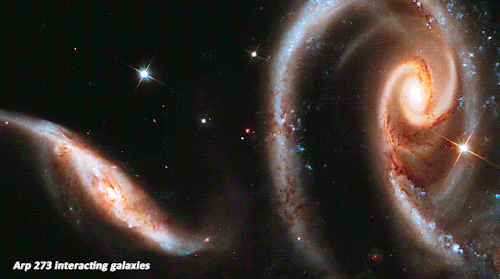




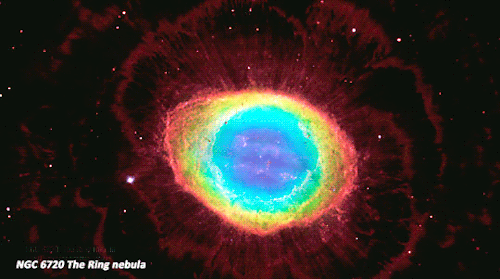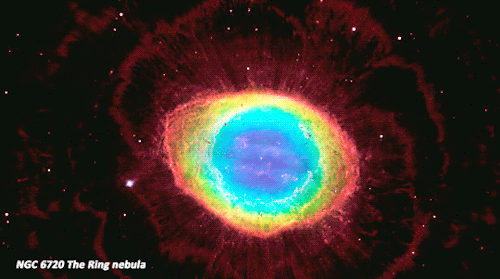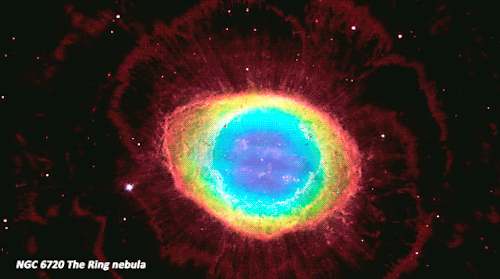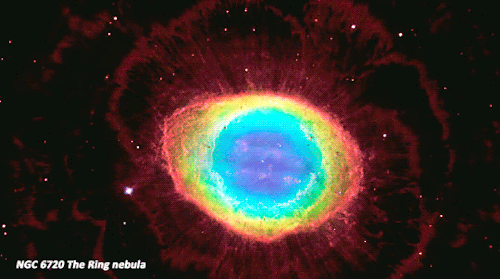


The Best of Hubble_1



Messier 1 - The Crab Nebula
Potentially Humanity’s First Historically Observed Supernova
The Crab Nebula is the first astronomical object identified with a historical supernova explosion. Around in the year 1054, Chinese astronomers identified a large bright object that suddenly and mysteriously appeared in the sky. The explosion was so bright that it was even visible during the day time.
700 years later the super nova remnant faded in brightness as it expanded and was nearly forgotten. The Super Nova Remnant was rediscovered in 1758 ( officially re-recorded) by Charles Messier while he was creating a catalog of mysterious objects that looked like comets but were not.
We now know that the beautiful Crab Nebula is the magnificent result of the death of a star, which was unknown to Charles Messier and the Chinese Astronomers that discovered the Object. Now, thanks to space telescopes such as Hubble and Chandra, we can image the Nebula in great detail. The bottom left image is of a small region of the Crab Nebula. It shows “Rayleigh–Taylor instabilities in its intricate filamentary structure” and gives scientists a better understanding of the death of stars. The image to the bottom left shows combined visible light data from Hubble and x-ray data from Chandra.
Credit: NASA/Hubble/Chandra
Pride Flags Colorpicked from Nebulas





















