Experience Tumblr like never before
Radiation - Blog Posts




Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologicos a una nueva entrega en la que hablaremos sobre el asunto de Japón y las aguas residuales al mar una vez dicho esto pongan cómodos que empezamos. - Hace poco están en todos los medios de comunicación del mundo, que Japón tiene luz verde por la ONU para verter agua tratada en la planta nuclear de Fukushima en el accidente acontecido en 2011. - Hay más de 1.000 tanques y 1,34 millones de toneladas, posiblemente al 98% de la capacidad, además se está analizando el agua de mar y los alrededores de la central nuclear, actualmente se está analizando la concentración de tritio, los resultados estarán disponibles el día 25 por la tarde, previamente se habían tomado muestras de agua de los depósitos dando como resultado que era seguro, pero posiblemente tendrían que haber esperado más tiempo. - La población japonesa, se manifiesta al respecto porque esto va a generar problemas a largo plazo a la economía mundial. China suspende todas las importaciones de productos del mar japoneses, no se iba a quedar de brazos cruzados ¿Qué opinan ustedes al respecto? - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana.
考古学の日本研究者の皆様、ようこそ!今回は、日本と海への汚水問題についてお話しします。
最近、日本が2011年の福島原発事故の処理水を海洋投棄することを国連から許可されたことが世界中のメディアを賑わせている。
タンクは1000基以上、134万トンあり、おそらく容量の98%であろう。また、海水と原発周辺は分析中で、現在はトリチウムの濃度が分析されており、25日の午後に結果が出る予定である。以前は貯水池から水を採取し、安全であるという結果を出していたが、おそらくもっと待つべきだったのだろう。
日本国民が抗議しているのは、これが世界経済に長期的な問題を引き起こすからである。中国が日本産水産物の輸入を全面的に停止したのだから、黙って見過ごすわけがない。 これについてどう思う?
お気に召していただけたなら幸いである。 それではまた、良い一週間を。
Welcome, japonistasarqueologicos to a new installment in which we will talk about the issue of Japan and sewage into the sea, that said, make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - It has recently been all over the world's media that Japan has been given the green light by the UN to dump treated water into the Fukushima nuclear power plant from the 2011 accident. - There are more than 1,000 tanks and 1.34 million tons, possibly at 98% of capacity, also the sea water and the surroundings of the nuclear plant are being analysed, currently the concentration of tritium is being analysed, the results will be available on the 25th in the afternoon, previously water samples had been taken from the reservoirs giving as a result that it was safe, but possibly they should have waited longer. - The Japanese people are protesting because this is going to create long-term problems for the world economy. China suspends all imports of Japanese seafood, they are not going to sit back and do nothing. What do you think about this? - I hope you liked it and I'll see you in future posts. Have a good week.
Medic wears x-ray shield gloves.
i have been wondering what kind of gloves medic wears for so long and it hit me: they look just like radiation protection gloves!!
propaganda:
medic’s gloves are way thicker than most rubber gloves, they don’t appear to be normal fabric, and they’re very angular. x-ray gloves are the same. observe our beloved doc:



and check out these:



do you see!? do you see the vision??
(propaganda for the mediguns being tubes in next reblog bc image limit)
Yummy 😋
It's Elephants Foot Friday!!!!

RB to instantly receive 8000 roentgens of radiation

Hopefully looking forward for the upcoming adventure I guess next year already...badabam #stalker #shadowofchernobyl #radiation #radioactive #radioactivity #anomaly #adventure https://www.instagram.com/p/CWJJvSkITYodO0qAcVnIl_LFriu4vAzzArRtso0/?utm_medium=tumblr
Farewell to the Van Allen Probes
After seven years of studying the radiation around Earth, the Van Allen Probes spacecraft have retired.

Originally slated for a two-year mission, these two spacecraft studied Earth's radiation belts — giant, donut-shaped clouds of particles surrounding Earth — for nearly seven years. The mission team used the last of their propellant this year to place the spacecraft into a lower orbit that will eventually decay, allowing the Van Allen Probes to re-enter and burn up in Earth's atmosphere.

Earth's radiation belts exist because energized charged particles from the Sun and other sources in space become trapped in our planet's huge magnetic field, creating vast regions around Earth that teem with radiation. This is one of the harshest environments in space — and the Van Allen Probes survived more than three times longer than planned orbiting through this intense region.
The shape, size and intensity of the radiation belts change, meaning that satellites — like those used for telecommunications and GPS — can be bombarded with a sudden influx of radiation. The Van Allen Probes shed new light on what invisible forces drive these changes — like waves of charged particles and electromagnetic fields driven by the Sun, called space weather.

Here are a few scientific highlights from the Van Allen Probes — from the early days of the mission to earlier this year:
The Van Allen belts were first discovered in 1958, and for decades, scientists thought there were only two concentric belts. But, days after the Van Allen Probes launched, scientists discovered that during times of intense solar activity, a third belt can form.
The belts are composed of charged particles and electromagnetic fields and can be energized by different types of plasma waves. One type, called electrostatic double layers, appear as short blips of enhanced electric field. During one observing period, Probe B saw 7,000 such blips repeatedly pass over the spacecraft in a single minute!
During big space weather storms, which are ultimately caused by activity on the Sun, ions — electrically charged atoms or molecules — can be pushed deep into Earth’s magnetosphere. These particles carry electromagnetic currents that circle around the planet and can dramatically distort Earth’s magnetic field.

Across space, fluctuating electric and magnetic fields can create what are known as plasma waves. These waves intensify during space weather storms and can accelerate particles to incredible speeds. The Van Allen Probes found that one type of plasma wave known as hiss can contribute greatly to the loss of electrons from the belts.
The Van Allen belts are composed of electrons and ions with a range of energies. In 2015, research from the Van Allen Probes found that, unlike the outer belt, there were no electrons with energies greater than a million electron volts in the inner belt.
Plasma waves known as whistler chorus waves are also common in our near-Earth environment. These waves can travel parallel or at an angle to the local magnetic field. The Van Allen Probes demonstrated the two types of waves cannot be present simultaneously, resulting in greater radiation belt particle scattering in certain areas.
Very low frequency chorus waves, another variety of plasma waves, can pump up the energy of electrons to millions of electronvolts. During storm conditions, the Van Allen Probes found these waves can hugely increase the energy of particles in the belts in just a few hours.

Scientists often use computer simulation models to understand the physics behind certain phenomena. A model simulating particles in the Van Allen belts helped scientists understand how particles can be lost, replenished and trapped by Earth’s magnetic field.
The Van Allen Probes observed several cases of extremely energetic ions speeding toward Earth. Research found that these ions’ acceleration was connected to their electric charge and not to their mass.
The Sun emits faster and slower gusts of charged particles called the solar wind. Since the Sun rotates, these gusts — the fast wind — reach Earth periodically. Changes in these gusts cause the extent of the region of cold ionized gas around Earth — the plasmasphere — to shrink. Data from the Van Allen Probes showed that such changes in the plasmasphere fluctuated at the same rate as the solar rotation — every 27 days.
Though the mission has ended, scientists will use data from the Van Allen Probes for years to come. See the latest Van Allen Probes science at nasa.gov/vanallen.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Facts About Earth's Radiation Donuts 🍩
Did you know that our planet is surrounded by giant, donut-shaped clouds of radiation?

Here's what you need to know.
1. The radiation belts are a side effect of Earth's magnetic field

The Van Allen radiation belts exist because fast-moving charged particles get trapped inside Earth's natural magnetic field, forming two concentric donut-shaped clouds of radiation. Other planets with global magnetic fields, like Jupiter, also have radiation belts.
2. The radiation belts were one of our first Space Age discoveries

Earth's radiation belts were first identified in 1958 by Explorer 1, the first U.S. satellite. The inner belt, composed predominantly of protons, and the outer belt, mostly electrons, would come to be named the Van Allen Belts, after James Van Allen, the scientist who led the charge designing the instruments and studying the radiation data from Explorer 1.
3. The Van Allen Probes have spent six years exploring the radiation belts

In 2012, we launched the twin Van Allen Probes to study the radiation belts. Over the past six years, these spacecraft have orbited in and out of the belts, providing brand-new data about how the radiation belts shift and change in response to solar activity and other factors.
4. Surprise! Sometimes there are three radiation belts

Shortly after launch, the Van Allen Probes detected a previously-unknown third radiation belt, created by a bout of strong solar activity. All the extra energy directed towards Earth meant that some particles trapped in our planet's magnetic field were swept out into the usually relatively empty region between the two Van Allen Belts, creating an additional radiation belt.
5. Swan song for the Van Allen Probes

Originally designed for a two-year mission, the Van Allen Probes have spent more than six years collecting data in the harsh radiation environment of the Van Allen Belts. In spring 2019, we're changing their orbit to bring the perigee — the part of the orbit where the spacecraft are closest to Earth — about 190 miles lower. This ensures that the spacecraft will eventually burn up in Earth's atmosphere, instead of orbiting forever and becoming space junk.
Because the Van Allen Probes have proven to be so hardy, they'll continue collecting data throughout the final months of the mission until they run out of fuel. As they skim through the outer reaches of Earth's atmosphere, scientists and engineers will also learn more about how atmospheric oxygen can degrade satellite measurements — information that can help build better satellites in the future.
Keep up with the latest on the mission on Twitter, Facebook or nasa.gov/vanallenprobes.
Human Research, Robotic Refueling, Crystallography and More Headed to Orbiting Lab
New science is headed to the International Space Station aboard the SpaceX Dragon.
Investigations on this flight include a test of robotic technology for refueling spacecraft, a project to map the world’s forests and two student studies inspired by Marvel’s “Guardians of the Galaxy” series.
Learn more about the science heading into low-Earth orbit:
The forest is strong with this one: GEDI studies Earth’s forests in 3D
The Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) is an instrument to measure and map Earth’s tropical and temperate forests in 3D.

The Jedi knights may help protect a galaxy far, far away, but our GEDI will help us study and understand forest changes right here on Earth.
Robotic refueling in space
What’s cooler than cool? Cryogenic propellants, or ice-cold spacecraft fuel! Our Robotic Refueling Mission 3 (RRM3) will demonstrate technologies for storing and transferring these special liquids. By establishing ways to replenish this fuel supply in space, RRM3 could help spacecraft live longer and journey farther.

The mission’s techniques could even be applied to potential lunar gas stations at the Moon, or refueling rockets departing from Mars.
Staying strong in space
The Molecular Muscle investigation examines the molecular causes of muscle abnormalities from spaceflight in C. elgans, a roundworm and model organism.
This study could give researchers a better understanding of why muscles deteriorate in microgravity so they can improve methods to help crew members maintain their strength in space.

Investigation studies space-grown crystals for protection against radiation
Perfect Crystals is a study to learn more about an antioxidant protein called manganese superoxide dismutase that protects the body from the effects of radiation and some harmful chemicals.
The station’s microgravity environment allows researchers to grow more perfectly ordered crystals of the proteins. These crystals are brought back to Earth and studied in detail to learn more about how the manganese superoxide dismutase works. Understanding how this protein functions may aid researchers in developing techniques to reduce the threat of radiation exposure to astronauts as well as prevent and treat some kinds of cancers on Earth.
Satellite deployment reaching new heights with SlingShot
SlingShot is a new, cost-effective commercial satellite deployment system that will be tested for the first time.

SlingShot hardware, two small CubeSats, and a hosted payload will be carried to the station inside SpaceX’s Dragon capsule and installed on a Cygnus spacecraft already docked to the orbiting laboratory. Later, Cygnus will depart station and fly to a pre-determined altitude to release the satellites and interact with the hosted payload.
Investigation studies accelerated aging in microgravity
Spaceflight appears to accelerate aging in both humans and mice. Rodent Research-8 (RR-8) is a study to understand the physiology of aging and the role it plays on the progression of disease in humans. This investigation could provide a better understanding of how aging changes the body, which may lead to new therapies for related conditions experienced by astronauts in space and people on Earth.
Guardians of the space station: Student contest flies to orbiting lab
The MARVEL ‘Guardians of the Galaxy’ Space Station Challenge is a joint project between the U.S. National Laboratory and Marvel Entertainment featuring two winning experiments from a contest for American teenage students. For the contest, students were asked to submit microgravity experiment concepts that related to the Rocket and Groot characters from Marvel’s “Guardians of the Galaxy” comic book series.

Team Rocket: Staying Healthy in Space
If an astronaut suffers a broken tooth or lost filling in space, they need a reliable and easy way to fix it. This experiment investigates how well a dental glue activated by ultraviolet light would work in microgravity. Researchers will evaluate the use of the glue by treating simulated broken teeth and testing them aboard the station.
Team Groot: Aeroponic Farming in Microgravity
This experiment explores an alternative method for watering plants in the absence of gravity using a misting device to deliver water to the plant roots and an air pump to blow excess water away. Results from this experiment may enable humans to grow fruits and vegetables in microgravity, and eliminate a major obstacle for long-term spaceflight.
These investigation join hundreds of others currently happening aboard the station. For more info, follow @ISS_Research!
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Space Radiation: Hazard of Stealth
A human journey to Mars, at first glance, offers an inexhaustible amount of complexities. To bring a mission to the Red Planet from fiction to fact, our Human Research Program has organized hazards astronauts will encounter on a continual basis into five classifications.

The first hazard of a human mission to Mars is also the most difficult to visualize because, well, space radiation is invisible to the human eye. Radiation is not only stealthy, but considered one of the most menacing of the five hazards.



Above Earth’s natural protection, radiation exposure increases cancer risk, damages the central nervous system, can alter cognitive function, reduce motor function and prompt behavioral changes. To learn what can happen above low-Earth orbit, we study how radiation affects biological samples using a ground-based research laboratory.


Exploration to the Moon and Mars will expose astronauts to five known hazards of spaceflight, including radiation. To learn more, and find out what our Human Research Program is doing to protect humans in space, check out the "Hazards of Human Spaceflight" website or check out this week’s episode of “Houston We Have a Podcast,” in which our host Gary Jordan further dives into the threat of radiation with Zarana Patel, a radiation lead scientist at the Johnson Space Center.

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Why We Study the Sun-Earth Connection – Explained Through Songs
We're launching a new mission to the International Space Station to continue measurements of the Sun's energy reaching Earth.

The Total and Spectral solar Irradiance Sensor (TSIS-1) will precisely measure the total amount of sunlight that falls on Earth and how that light is distributed among different wavelengths, including the ultraviolet, visible and infrared. This will give us a better understanding of Earth’s primary energy supply and help improve models simulating Earth’s climate.
1. You are my sunshine, my only sunshine. You make me happy when skies are gray.

The Sun is Earth's sunshine and it does more than make us happy; it gives us life. Our Sun's energy drives our planet's ocean currents, seasons, weather and climate. Changes in the Sun also alter our climate in at least two ways.
First, solar radiation has a direct effect where it heats regions of Earth, like our oceans, land, and atmosphere. Second, the solar radiation can cause indirect effects, such as when sunlight interacts with molecules in the upper atmosphere to produce ozone which can affect human health.

Earth’s energy system is in a constant dance to maintain a balance between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing energy from Earth to space, which scientists call Earth’s energy budget. If you have more energy absorbed by the Earth than leaving it, its temperature increases and vice versa. Because the Sun is Earth's fundamental energy source and only sunshine, we need a quantitative record of the Sun's solar energy output. TSIS-1 will provide the most accurate measurements ever made of sunlight as seen from above Earth’s atmosphere.
2. You're hot then you're cold…You're in then you're out. You're up then you're down.

The energy flow between the Earth and Sun's connection is not a constant thing. The Sun can be fickle, sometimes it puts out slightly more energy and some years less. Earth is no better. The Earth absorbs different amounts of the Sun's energy depending on many factors, such as the presence of clouds and tiny particles in the atmosphere called aerosols.
What we do know is that the Sun's cycle is about 11 years rolling through periods of quiet to times of intense activity. When the Sun is super-intense it releases explosions of light and solar material. This time is a solar maximum.
When the Sun is in a quiet state this period is called the solar minimum.

Over the course of one solar cycle (one 11-year period), the Sun’s total emitted energy varies on average at about 0.1 percent. That may not sound like a lot, but the Sun emits a large amount of energy – 1,361 watts per square meter. Even fluctuations at just a tenth of a percent can affect Earth. That's why TSIS-1 is launching: to help scientists understand and anticipate how changes in the Sun will affect us on Earth.
3. You're so vain. You probably think this climate model is about you.

Scientists use computer models to interpret changes in the Sun’s energy input. If less solar energy is available, scientists can gauge how that affects Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, weather and seasons by using computer simulations. But the Sun is just one of many factors scientists use to model Earth’s climate. A lot of other factors come into play in addition to the energy from the Sun. Factors like greenhouse gases, clouds scattering light and small particles in the atmosphere called aerosols all can affect Earth’s climate so they all need to be included in climate models. So, while we need to measure the total amount of energy from the Sun, we also need to understand how these other factors alter the amount of energy reaching Earth's surface and affect our climate.
4. Someday we'll find it, the rainbow connection. The lovers, the dreamers and me.

We receive the Sun's energy in many different wavelengths, including visible light (rainbows!) as well as light we can't see like infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths. Each color or wavelength of light from the Sun affects Earth’s atmosphere differently.
For instance, ultraviolet light from the Sun can affect Earth's ozone. High in the atmosphere is a layer of protective ozone gas. Ozone is Earth’s natural sunscreen, absorbing the Sun’s most harmful ultraviolet radiation and protecting living things below. But ozone is vulnerable to certain gases made by humans that reach the upper atmosphere. Once there, they react in the presence of sunlight to destroy ozone molecules. Currently, several satellites from us and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) track the ozone in the upper atmosphere and the solar energy that drives the photochemistry that creates and destroys ozone. Our new instrument, TSIS-1, will join that fleet with even better accuracy.

TSIS-1 will see different types of ultraviolet (UV) light, including UV-B and UV-C. Each plays a different role in the ozone layer. UV-C rays are essential in creating ozone. UV-B rays and some naturally occurring chemicals regulate the abundance of ozone in the upper atmosphere. The amount of ozone is a balance between these natural production and loss processes.
TSIS-1 data of the Sun's UV energy will help improve computer models of the atmosphere that need accurate measurements of sunlight across the ultraviolet spectrum to model the ozone layer correctly. While UV light represents a tiny fraction of the total sunlight that reaches the top of Earth's atmosphere, it fluctuates from 3 to 10 percent, a change that, in turn causes small changes in the chemical composition and thermal structure of the upper atmosphere.
This is just one of the important applications of TSIS-1 measurements. TSIS-1 will measure how the Sun's energy is distributed over 1,000 different wavelengths.
5. Every move you make…every step you take, I'll be watching you.

TSIS-1 will continue our nearly 40 years of closely studying the total amount of energy the Sun sends to Earth from space. We've previously studied this 'total solar irradiance' with nine previous satellites, currently with Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, (SORCE).

NASA’s SORCE collected this data on the total amount of the Sun’s radiant energy throughout Sept. 2017. The satellite actually detected a dip in total irradiance – or the total amount of energy from the Sun- during the month’s intense solar activity.
But there's still very much we don't know about total solar irradiance. We do not know how it varies over longer timescales. Longer term observations are especially important because scientists have observed unusually quiet magnetic activity from the Sun for the past two decades with previous satellites. During the last prolonged solar minimum in 2008-2009, our Sun was the quietest it has ever been since we started observations in 1978. Scientists expect the Sun to enter a solar minimum within the next three years, and TSIS-1 will be primed to take measurements of the next minimum and see if this is part of a larger trend.
For all the latest Earth updates, follow us on Twitter @NASAEarth or Facebook.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
September 2017 Was 🔥 on the Sun
The Sun started September 2017 with flair, emitting 31 sizable solar flares and releasing several powerful coronal mass ejections, or CMEs, between Sept. 6-10.

Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth’s atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however — when intense enough — they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.

CMEs are massive clouds of solar material and magnetic fields that erupt from the Sun at incredible speeds. Depending on the direction they’re traveling in, CMEs can spark powerful geomagnetic storms in Earth’s magnetic field.
As always, we and our partners had many missions observing the Sun from both Earth and space, enabling scientists to study these events from multiple perspectives. With this integrated picture of solar activity, scientists can better track the evolution of solar eruptions and work toward improving our understanding of space weather.

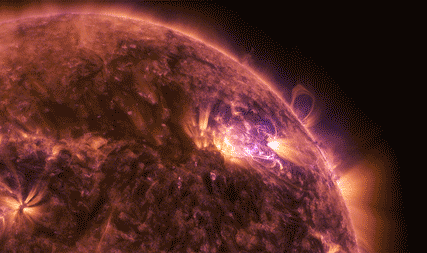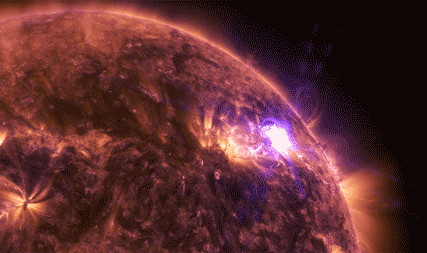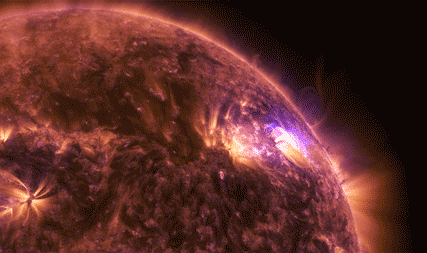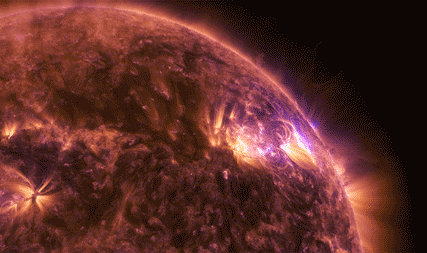
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-16, or GOES-16, watches the Sun’s upper atmosphere — called the corona — at six different wavelengths, allowing it to observe a wide range of solar phenomena. GOES-16 caught this footage of an X9.3 flare on Sept. 6, 2017.
This was the most intense flare recorded during the current 11-year solar cycle. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, and so on. GOES also detected solar energetic particles associated with this activity.

Our Solar Dynamics Observatory captured these images of X2.2 and X9.3 flares on Sept. 6, 2017, in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light that shows solar material heated to over one million degrees Fahrenheit.

JAXA/NASA’s Hinode caught this video of an X8.2 flare on Sept. 10, 2017, the second largest flare of this solar cycle, with its X-ray Telescope. The instrument captures X-ray images of the corona to help scientists link changes in the Sun’s magnetic field to explosive solar events like this flare.

Key instruments aboard our Solar and Terrestrial Relations Observatory, or STEREO, include a pair of coronagraphs — instruments that use a metal disk called an occulting disk to study the corona. The occulting disk blocks the Sun’s bright light, making it possible to discern the detailed features of the Sun’s outer atmosphere and track coronal mass ejections as they erupt from the Sun.
On Sept. 9, 2017, STEREO watched a CME erupt from the Sun. The next day, STEREO observed an even bigger CME. The Sept. 10 CME traveled away from the Sun at calculated speeds as high as 7 million mph, and was one of the fastest CMEs ever recorded. The CME was not Earth-directed: It side-swiped Earth’s magnetic field, and therefore did not cause significant geomagnetic activity. Mercury is in view as the bright white dot moving leftwards in the frame.

Like STEREO, ESA/NASA’s Solar and Heliospheric Observatory, or SOHO, uses a coronagraph to track solar storms. SOHO also observed the CMEs that occurred during Sept. 9-10, 2017; multiple views provide more information for space weather models. As the CME expands beyond SOHO’s field of view, a flurry of what looks like snow floods the frame. These are high-energy particles flung out ahead of the CME at near-light speeds that struck SOHO’s imager.

Our Interface Region Imaging Spectrometer, or IRIS, captured this video on Sept. 10, 2017, showing jets of solar material swimming down toward the Sun’s surface. These structures are sometimes observed in the corona during solar flares, and this particular set was associated with the X8.2 flare of the same day.

Our Solar Radiation and Climate Experiment, or SORCE, collected the above data on total solar irradiance, the total amount of the Sun’s radiant energy, throughout Sept. 2017. While the Sun produced high levels of extreme ultraviolet light, SORCE actually detected a dip in total irradiance during the month’s intense solar activity.
A possible explanation for this observation is that over the active regions — where solar flares originate — the darkening effect of sunspots is greater than the brightening effect of the flare’s extreme ultraviolet emissions. As a result, the total solar irradiance suddenly dropped during the flare events.
Scientists gather long-term solar irradiance data in order to understand not only our dynamic star, but also its relationship to Earth’s environment and climate. We are ready to launch the Total Spectral solar Irradiance Sensor-1, or TSIS-1, this December to continue making total solar irradiance measurements.

The intense solar activity also sparked global aurora on Mars more than 25 times brighter than any previously seen by NASA’s Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution, or MAVEN, mission. MAVEN studies the Martian atmosphere’s interaction with the solar wind, the constant flow of charged particles from the Sun. These images from MAVEN’s Imaging Ultraviolet Spectrograph show the appearance of bright aurora on Mars during the September solar storm. The purple-white colors show the intensity of ultraviolet light on Mars’ night side before (left) and during (right) the event.
For all the latest on solar and space weather research, follow us on Twitter @NASASun or Facebook.
GOES images are courtesy of NOAA. Hinode images are courtesy of JAXA and NASA. SOHO images are courtesy of ESA and NASA.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Exploring the Invisible: Magnetic Reconnection
People always say that space is a vacuum. That’s true – space is about a thousand times emptier than even the best laboratory vacuums on Earth. Even so, space contains lots of stuff we can’t see. We study this invisible space stuff because we need to understand it to safely send technology and astronauts into space.
The stuff that fills space is mostly plasma, which is gas where particles have separated into positive ions and negative electrons, creating a sea of electrically-charged particles. This plasma also contains something else – magnetic fields.

The particles in space can reach very high speeds, creating radiation. One of the main engines that drives that acceleration to high speeds is called magnetic reconnection. But what is magnetic reconnection?
Magnetic reconnection happens when two oppositely-aligned magnetic fields pinch together and explosively realign. As the lines snap into their new configuration – as in the animation below – the sudden change sends electrons and ions flying at incredible speeds.

Magnetic reconnection releases energy. We can't see the energy itself, but we can see the results: It can set off solar explosions – such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections – or disturbances near Earth that cause auroras.
In March 2015, we launched the four Magnetospheric Multiscale, or MMS, spacecraft on a mission to study magnetic reconnection. Magnetic reconnection only happens in a vacuum with ionized gas. These conditions are vanishingly rare on Earth, so we went to space to study this explosive process.
Because MMS has four separate – but essentially identical – spacecraft, it can watch magnetic reconnection in three dimensions.

The below animation shows what MMS sees – the magnetic fields are magenta, positive ions are purple, and electrons are yellow. The arrows show which the direction the fields and particles are moving.

Like how a research plane flies through a hurricane, MMS flew directly through a magnetic reconnection event in October 2015.
In the data visualization below, you can see the magnetic reconnection happening as the yellow arrows (which represent electrons) explode in all directions. You’ll notice that the magnetic field (represented by magenta arrows) changes direction after the magnetic reconnection, showing that the magnetic field has reconfigured.

Magnetic reconnection transfers energy into Earth’s atmosphere – but it’s not inherently dangerous. Sometimes, the changes in Earth’s magnetic field caused by magnetic reconnection can create electric currents that put a strain on power systems. However, the energy released is more often channeled into auroras, the multicolored lights that most often appear near the North and South Poles.

As the MMS mission continues the four spacecraft can be moved closer together or farther apart, letting us measure magnetic reconnection on all different scales. Each set of observations contributes to explaining different aspects of this invisible phenomenon of magnetic reconnection. Together, the information will help scientists better map out our space environment — crucial information as we journey ever farther beyond our home planet.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
5 Facts About Earth's Radiation Donuts 🍩
Did you know that our planet is surrounded by giant, donut-shaped clouds of radiation?

Here’s what you need to know.
1. The radiation belts are a side effect of Earth’s magnetic field

The Van Allen radiation belts exist because fast-moving charged particles get trapped inside Earth’s natural magnetic field, forming two concentric donut-shaped clouds of radiation. Other planets with global magnetic fields, like Jupiter, also have radiation belts.
2. The radiation belts were one of our first Space Age discoveries

Earth’s radiation belts were first identified in 1958 by Explorer 1, the first U.S. satellite. The inner belt, composed predominantly of protons, and the outer belt, mostly electrons, would come to be named the Van Allen Belts, after James Van Allen, the scientist who led the charge designing the instruments and studying the radiation data from Explorer 1.
3. The Van Allen Probes have spent six years exploring the radiation belts

In 2012, we launched the twin Van Allen Probes to study the radiation belts. Over the past six years, these spacecraft have orbited in and out of the belts, providing brand-new data about how the radiation belts shift and change in response to solar activity and other factors.
4. Surprise! Sometimes there are three radiation belts

Shortly after launch, the Van Allen Probes detected a previously-unknown third radiation belt, created by a bout of strong solar activity. All the extra energy directed towards Earth meant that some particles trapped in our planet’s magnetic field were swept out into the usually relatively empty region between the two Van Allen Belts, creating an additional radiation belt.
5. Swan song for the Van Allen Probes

Originally designed for a two-year mission, the Van Allen Probes have spent more than six years collecting data in the harsh radiation environment of the Van Allen Belts. In spring 2019, we’re changing their orbit to bring the perigee — the part of the orbit where the spacecraft are closest to Earth — about 190 miles lower. This ensures that the spacecraft will eventually burn up in Earth’s atmosphere, instead of orbiting forever and becoming space junk.
Because the Van Allen Probes have proven to be so hardy, they’ll continue collecting data throughout the final months of the mission until they run out of fuel. As they skim through the outer reaches of Earth’s atmosphere, scientists and engineers will also learn more about how atmospheric oxygen can degrade satellite measurements — information that can help build better satellites in the future.
Keep up with the latest on the mission on Twitter, Facebook or nasa.gov/vanallenprobes.


Cloud Chambers: Visualizing Radiation
The cloud chamber, also known as the Wilson chamber, is a particle detector used for detecting ionizing radiation.
In its most basic form, a cloud chamber is a sealed environment containing a supersaturated vapor of water or alcohol. When a charged particle (for example, an alpha or beta particle) interacts with the mixture, the fluid is ionized. The resulting ions act as condensation nuclei, around which a mist will form (because the mixture is on the point of condensation).
The high energies of alpha and beta particles mean that a trail is left, due to many ions being produced along the path of the charged particle. These tracks have distinctive shapes, for example, an alpha particle’s track is broad and shows more evidence of deflection by collisions, while an electron’s is thinner and straight. -(x)
More science and gifs on my blog: rudescience Gif made from: This video by The Royal Institution References: (x), (x).

~Who we want to be~ #deep #thoughts #realization #life #purpose #soul #radiation #energy #belief #cosmos #snow #solitude #nature #naturephotography #naturelovers #photooftheday #photography #travel #instatravel #discover #explore #observe #silence #cosmos #creation #winter #wanderlust #world #usa #natgeo #traveltheworld

