Experience Tumblr like never before
Spacetech - Blog Posts
NASA’s 60th Anniversary: Trailblazing Technology
Technology drives exploration. For 60 years, we have advanced technology to meet the rigorous needs of our missions. From GPS navigation to water filtration systems, our technologies developed for space improve your daily life on Earth. We continue to innovate and explore. Since we opened for business on Oct. 1, 1958, our history tells a story of exploration, innovation and discoveries. The next 60 years, that story continues. Learn more: https://www.nasa.gov/60
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Five NASA Technologies at the 2017 Consumer Electronics Show
This week, we’re attending the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES), where we’re joining industrial pioneers and business leaders from across the globe to showcase our space technology. Since 1967, CES has been the place to be for next-generation innovations to get their marketplace debut.
Our technologies are driving exploration and enabling the agency’s bold new missions to extend the human presence beyond the moon, to an asteroid, to Mars and beyond. Here’s a look at five technologies we’re showing off at #CES2017:
1. IDEAS
Our Integrated Display and Environmental Awareness System (IDEAS) is an interactive optical computer that works for smart glasses. The idea behind IDEAS is to enhance real-time operations by providing augmented reality data to field engineers here on Earth and in space.

This device would allow users to see and modify critical information on a transparent, interactive display without taking their eyes or hands off the work in front of them.

This wearable technology could dramatically improve the user’s situational awareness, thus improving safety and efficiency.

For example, an astronaut could see health data, oxygen levels or even environmental emergencies like “invisible” ethanol fires right on their helmet view pane.

And while the IDEAS prototype is an innovative solution to the challenges of in-space missions, it won’t just benefit astronauts—this technology can be applied to countless fields here on Earth.
2. VERVE
Engineers at our Ames Research Center are developing robots to work as teammates with humans.

They created a user interface called the Visual Environment for Remote Virtual Exploration (VERVE) that allows researchers to see from a robot’s perspective.

Using VERVE, astronauts on the International Space Station remotely operated the K10 rover—designed to act as a scout during NASA missions to survey terrain and collect science data to help human explorers.

This week, Nissan announced that a version of our VERVE was modified for its Seamless Autonomous Mobility (SAM), a platform for the integration of autonomous vehicles into our society. For more on this partnership: https://www.nasa.gov/ames/nisv-podcast-Terry-Fong
3. OnSight
Did you know that we are leveraging technology from virtual and augmented reality apps to help scientists study Mars and to help astronauts in space?

The Ops Lab at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory is at the forefront of deploying these groundbreaking applications to multiple missions.

One project we’re demonstrating at CES, is how our OnSight tool—a mixed reality application developed for the Microsoft HoloLens—enables scientists to “work on Mars” together from their offices.

Supported by the Mars 2020 and Curiosity missions, it is currently in use by a pilot group of scientists for rover operations. Another HoloLens project is being used aboard the International Space Station to empower the crew with assistance when and where they need it.

At CES, we’re also using the Oculus Rift virtual reality platform to provide a tour from the launchpad at our Kennedy Space Center of our Space Launch System (SLS). SLS will be the world’s most powerful rocket and will launch astronauts in the Orion Spacecraft on missions to an asteroid and eventually to Mars. Engineers continue to make progress aimed toward delivering the first SLS rocket to Kennedy in 2018.
4. PUFFER
The Pop-Up Flat Folding Explorer Robot, PUFFER, is an origami-inspired robotic technology prototype that folds into the size of a smartphone.

It is a low-volume, low-cost enhancement whose compact design means that many little robots could be packed in to a larger “parent” spacecraft to be deployed on a planet’s surface to increase surface mobility. It’s like a Mars rover Mini-Me!

5. ROV-E
Our Remote Operated Vehicle for Education, or ROV-E, is a six-wheeled rover modeled after our Curiosity and the future Mars 2020 Rover.

It uses off-the-shelf, easily programmable computers and 3D-printed parts. ROV-E has four modes, including user-controlled driving to sensor-based hazard-avoidance and “follow me” modes. ROV-E can answer questions about Mars and follow voice commands.
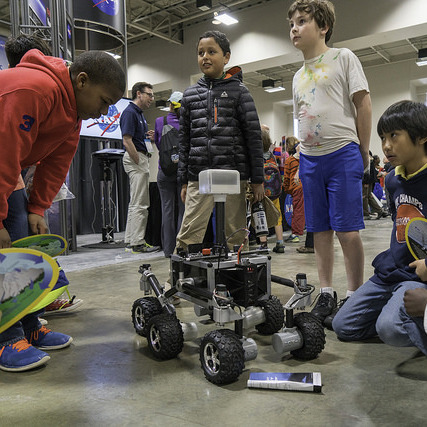

ROV-E was developed by a team of interns and young, up-and-coming professionals at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory who wanted to build a Mars rover from scratch to help introduce students and the public to Science, Technology, Engineering & Mathematics (STEM) careers, planetary science and our Journey to Mars.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
LETS DO IT TOGETHER NASA :)
Mission Possible: Redirecting an Asteroid
As part of our Asteroid Redirect Mission (ARM), we plan to send a robotic spacecraft to an asteroid tens of millions of miles away from Earth, capture a multi-ton boulder and bring it to an orbit near the moon for future crew exploration.
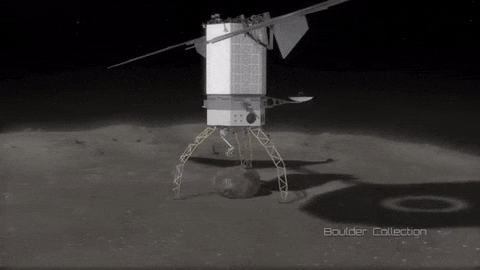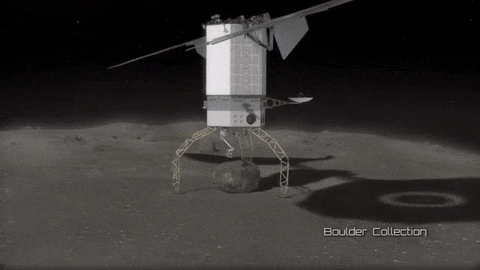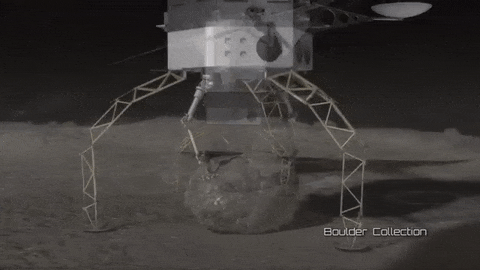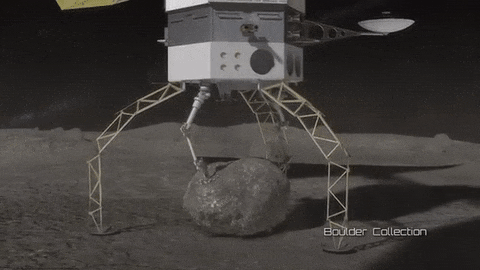
This mission to visit a large near-Earth asteroid is part of our plan to advance the new technologies and spaceflight experience needed for a human mission to the Martian system in the 2030s.
How exactly will it work?
The robotic spacecraft, powered by the most advanced solar electric propulsion system, will travel for about 18 months to the target asteroid.

After the spacecraft arrives and the multi-ton boulder is collected from the surface, the spacecraft will hover near the asteroid to create a gravitational attraction that will slightly change the asteroid’s trajectory.

After the enhanced gravity tractor demonstration is compete, the robotic vehicle will deliver the boulder into a stable orbit near the moon. During the transit, the boulder will be further imaged and studied by the spacecraft.

Astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft will launch on the Space Launch System rocket to explore the returned boulder.

Orion will dock with the robotic vehicle that still has the boulder in its grasp.

While docked, two crew members on spacewalks will explore the boulder and collect samples to bring back to Earth for further study.

The astronauts and collected samples will return to Earth in the Orion spacecraft.
How will ARM help us send humans to Mars in the 2030s?

This mission will demonstrate future Mars-level exploration missions closer to home and will fly a mission with technologies and real life operational constraints that we’ll encounter on the way to the Red Planet. A few of the capabilities it will help us test include:
Solar Electric Propulsion – Using advanced Solar Electric Propulsion (SEP) technologies is an important part of future missions to send larger payloads into deep space and to the Mars system. Unlike chemical propulsion, which uses combustion and a nozzle to generate thrust, SEP uses electricity from solar arrays to create electromagnetic fields to accelerate and expel charged atoms (ions) to create a very low thrust with a very efficient use of propellant.
Trajectory and Navigation – When we move the massive asteroid boulder using low-thrust propulsion and leveraging the gravity fields of Earth and the moon, we’ll validate critical technologies for the future Mars missions.
Advances in Spacesuits – Spacesuits designed to operate in deep space and for the Mars surface will require upgrades to the portable life support system (PLSS). We are working on advanced PLSS that will protect astronauts on Mars or in deep space by improving carbon dioxide removal, humidity control and oxygen regulation. We are also improving mobility by evaluating advances in gloves to improve thermal capacity and dexterity.
Sample Collection and Containment Techniques – This experience will help us prepare to return samples from Mars through the development of new techniques for safe sample collection and containment. These techniques will ensure that humans do not contaminate the samples with microbes from Earth, while protecting our planet from any potential hazards in the samples that are returned.
Rendezvous and Docking Capabilities – Future human missions to Mars will require new capabilities to rendezvous and dock spacecraft in deep space. We will advance the current system we’ve developed with the international partners aboard the International Space Station.
Moving from spaceflight a couple hundred miles off Earth to the proving ground environment (40,000 miles beyond the moon) will allow us to start accumulating experience farther than humans have ever traveled in space.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com