Experience Tumblr like never before
Mesopelagic Zone - Blog Posts

Squarenose Helmetfish
Scopelogadus beanii
The Squarenose Helmetfish is found between 800m to 4000m in the ocean. It received this unique name due to its scales reminding scientists of an armored helmet worn by medieval knights. It also has unusual holes around its face, and the white strands covering its face are sensory canals.
Photo credit: https://www.vistaalmar.es/especies-marinas/peces-extranos/449-que-peces-mas-extranos.html

Pram Bug
Phronima sedentaria
The Pram Bug is a deep sea amphipod that is located between 200 to 1000m in the ocean. It has a translucent exoskeleton and can see primarily blue light. It is also is contained in a hollowed out barrel that is used for protection and to house babies. The image above is a female pram bug carrying its young.
Photo Credit:https://ocean.si.edu/ocean-life/invertebrates/phronima-female-and-young


Deep Sea Arrow Worm
Eukrohnia hamata
Arrow worms are small, predatory marine worms that consume copepods, ostracods, and larvae. They resembles a clear, ink pen whizzing through the dark sea. Furthermore, they are found primarily in the Artic Ocean between 700m to 1200m. The picture on the bottom is its head. They have 8 hooks, which are used to grab prey and 25 posterior teeth. Even though the arrow worms are terrifying up close, they are only 4.5 cm in size.
Photo credit: http://www.arcodiv.org/watercolumn/chaetognaths/Eukrohnia_hamata.html


Physonect Siphonophore
Nanomia cara
The Physonect siphonophore has tiny, bubble shaped sacs that are filled with gas. The sacs are called pneumatophores and help this creature move through the deep ocean. It also has venomous tentacles that stun prey and over eighty stomachs. There are numerous amounts of these strange creatures along the east coast, and they have cause some fisheries to collapse. Furthermore, they can be found at depth between 400m to 1000m.
Photo credit: http://www.seawater.no/fauna/cnidaria/cara.html
https://www.mindenpictures.com/stock-photo-siphonophore-hydrozoan-cnidarian-nanomia-cara-atlantic-nectophores-naturephotography-image90194961.html


Lav Polyp
leuckartiara octona
The Lav Polypo is a jelly that comes in a variety of colors and shapes; it dwells about 200m in the deep ocean. The red mass inside its translucent bell is the jelly’s reproductive organs. Furthermore, it uses its dull, yellow tentacles can catch unsuspecting prey.
Photo credit: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/65935582019848580/
https://www.petjellyfish.co.uk/shop/live-jellyfish/leuckartiara-octona
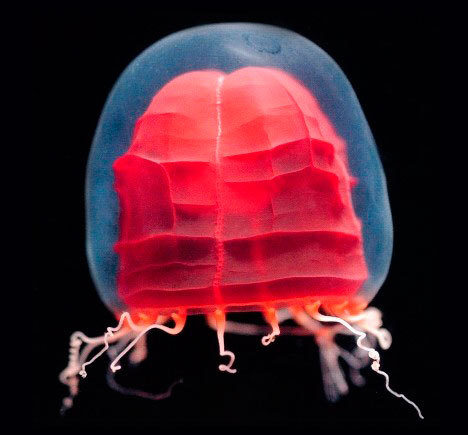

Red Paper Lantern Medusa
Pandea rubra
The Red Paper Lantern resembles a floating, Japanese paper lantern in the deep sea. It has the ability to crumple and wrinkle its bright, red bell, and it is located at depths between 550m to 1200m. It has also been nicknamed the “origami jelly.”
Photo credit: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Category:Pandea_rubra
http://www.thegorgeousdaily.com/pandea-rubra/


Pigbutt worm
Chaetopterus pugaporcinus
The Pigbutt worm or the flying buttocks of the sea is spotted floating between 965 m to 1300 m in the deep ocean. It is actually a polychaete (polly-keet) worm species that burrows in the ground as an adult, and floats around the ocean as a baby. The worm feeds itself : by creating a balloon of mucus; collecting particles on the mucus; and then consuming the particles. It is the rarest and thickest worm in the deep ocean, for only ten have been spotted.
Photocredit: https://roaring.earth/pigbutt-worm/


Black-devil anglerfish
Melanoncetus johnsoni
The Black-devil anglerfish is a skilled predator that lurks in the darkness. It uses a bioluminescent organ, a top its head, to lure unsuspecting prey into its jaws. Even though these fish are terrifying to look at, they are about the size of a grape fruit. To save energy, they remain immobile in the water, yet they can detect even the slightest vibrations. Since finding a mate is hard at this depth, male fish will attach themselves to a female and slowly dissolve into her tissue; so she is able to use the sperm the male provides at any time. In addition, this is the fish that tried to eat Marlin and Dory in “Finding Nemo.”
Photo credit: https://underthevastblueseas.tumblr.com/post/40882487364/this-female-black-devil-anglerfish-with-her-flabby
https://www.pinterest.fr/pin/574631233709001328/


Jewel Squid
Histioteuthis heteropsis
The Jewel Squid is covered in color-changing photophores that resemble sparkling gem stones. They also have a light-red coloration and are about 20 cm in length. They display a unique behavioral adaptation called diel migration. During the day, they stay at depths around 400-1200 m, and then surface during night (0-400m). This behavioral pattern is designed maximize feeding at night, and avoid predators during the day. The primary predator of the Jewel Squid is the Sperm Whale.
Photo credit: https://www.pinterest.com/pin/722827808920240115/
https://twitter.com/theoctonation/status/1168516522270253056


Giant Bell Jelly
Scrippsia pacifica
The Giant Belly Jelly has 256 tentacles attached to a gelatinous bell-shaped base. Like most cnidarians, the Giant Belly Jelly uses specialized stinging cells called nematocysts to catch its prey. When fish and other prey swim into its tentacles, the sensory projection on the cnidocyte (cell that holds the nematocysts) is activated. Then the nematocysts and barb are released, hitting the vulnerable prey and releasing a toxin into the prey’s body. The Giant Bell Jelly is found at 400 m in the ocean. It is related to the jellyfish, but it is categorized as a Hydrozoa (similar to the Portuguese- man-o-war)
https://vimeo.com/42551565
Photo Credit: https://www.pinterest.cl/pin/467107792572034837/
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/ivytech-bio1-1/chapter/phylum-cnidaria/


Glowing sucker octopus
Stauroteuthis syrtensis
The Glowing Sucker Octopus can be found at 2500 m in the deep ocean. This unique creature has two fins that look similar to elephant ears. They move elegantly through the water by moving these fins and contracting their mantle. Evidence of this creature has only been spotted in the Atlantic Ocean.
Photo credit: https://octolab.tv/species/glowing-sucker-octopus/
https://ferrebeekeeper.wordpress.com/2011/03/14/glowing-sucker-octopus/