Experience Tumblr like never before
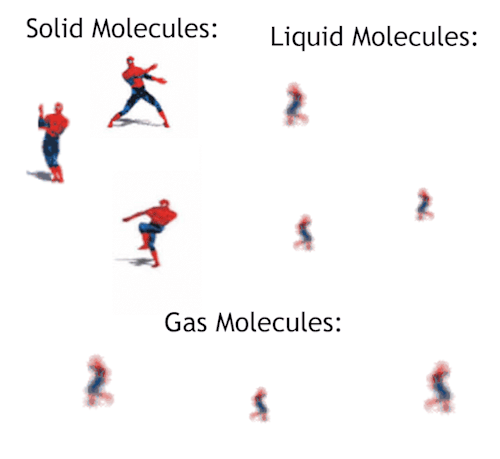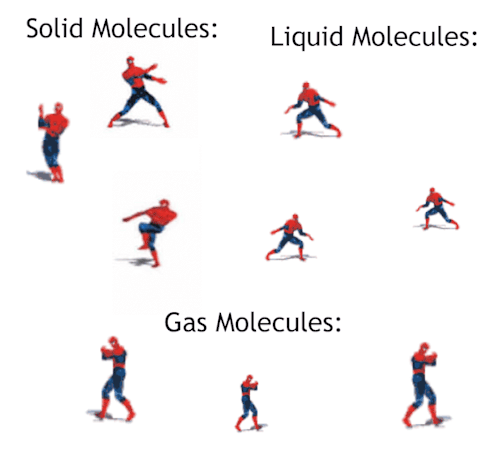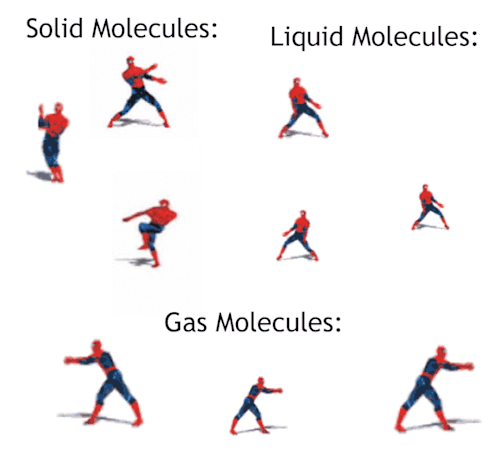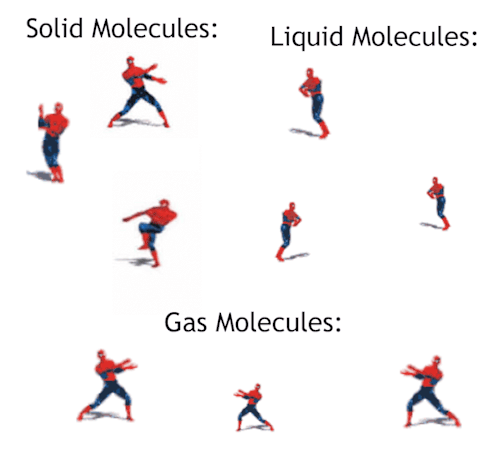
Gas - Blog Posts




braxxi but make it,,,, women!?
also some bonus stuff i drew a couple months ago, translating designs my beloved
Me gustan tus dibujos.
¿Sería molestia ver cómo dibujas a Gas?
Gracias! Y no me molestia nada
I always loved the heaters, I just never draw them 😅


Minneapolis Home Office Mid-sized minimalist built-in desk medium tone wood floor and brown floor home office library photo with white walls, a standard fireplace and a tile fireplace
Black Hole Sculpts an Hourglass Galaxy
When it comes to galaxies, our home, the Milky Way, is rather neat and orderly. Other galaxies can be much more chaotic. For example, the Markarian 573 galaxy has a black hole at its center which is spewing beams of light in opposite directions, giving its inner regions more of an hourglass shape.

Our scientists have long been fascinated by this unusual structure, seen above in optical light from the Hubble Space Telescope. Now their search has taken them deeper than ever — all the way into the super-sized black hole at the center of one galaxy.
So, what do we think is going on? When the black hole gobbles up matter, it releases a form of high-energy light called radiation (particularly in the form of X-rays), causing abnormal patterns in the flow of gas.
Let’s take a closer look.

Meet Markarian 573, the galaxy at the center of this image from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey, located about 240 million light-years away from Earth in the constellation Cetus. It’s the galaxy’s odd structure and the unusual motions of its components that inspire our scientists to study it.

As is the case with other so-called active galaxies, the ginormous black hole at the center of Markarian 573 likes to eat stuff. A thick ring of dust and gas accumulates around it, forming a doughnut. This ring only permits light to escape the black hole in two cone-shaped regions within the flat plane of the galaxy — and that’s what creates the hourglass, as shown in the illustration above.

Zooming out, we can see the two cones of emission (shown in gold in the animation above) spill into the galaxy's spiral arms (blue). As the galaxy rotates, gas clouds in the arms sweep through this radiation, which makes them light up so our scientists can track their movements from Earth.

What happens next depends on how close the gas is to the black hole. Gas that’s about 2,500 light-years from the black hole picks up speed and streams outward (shown as darker red and blue arrows). Gas that’s farther from the black hole also becomes ionized, but is not driven away and continues its motion around the galaxy as before.

Here is an actual snapshot of the inner region of Markarian 573, combining X-ray data (blue) from our Chandra X-ray Observatory and radio observations (purple) from the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array in New Mexico with a visible light image (gold) from our Hubble Space Telescope. Given its strange appearance, we’re left to wonder: what other funky shapes might far-off galaxies take?
For more information about the bizarre structure of Markarian 573, visit http://svs.gsfc.nasa.gov/12657
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com






I've posted it on instagram, sorry i was late but i did my first OC of Far Cry 5, hope you like it🐲🐉
it's my personal OC please ask before you want to use it, and if you want any information about other features about her, feel free to ask👍

Thermal Processes with Ideal Gas

SOOOOOOOOOO HAPPY HOW THIS TURNED OUT... I have always been a big BNHA fan since it first aird, and I’m soo happy that I’m capable of drawing my oc now.
Drawing done 22.02.2019.
- IF YOU TAKE DRAWINGS PLS GIVE ME CREDIT -
- Orihara Chiyo / Nora ♡
Instagram: @eleonorasapic



Carbon dioxide emissions in the UK are falling. CO2 emission fell 5.8% in 2016 from the previous year. Current emissions represent a 36% reduction from 1990 levels, and are at their lowest level since 1894 (outside the 1920s general strikes).
Why? The decline of coal. Coal use in the UK has declined steadily from its peak in 1956, and has experienced a dramatic decline since 2012. Coal use in 2016 dropped 52% from 2015.
The reduction in coal use is a result of multiple factors. The biggest is the expanded use of natural gas and renewables displacing coal. Other factors include an overall reduction in energy demand, the closing of Redcar Steelworks in 2015, and the UK’s carbon tax.
Source