High (Like 240,000 Miles) Fashion: What Astronauts Wear To The Moon
High (Like 240,000 Miles) Fashion: What Astronauts Wear to the Moon

We call it a spacesuit, almost as if it’s something an astronaut pulls out of the closet. It’s more accurate to think of it as an astronaut’s personal spacecraft: self-contained and functional, with a design focused on letting astronauts work safely in space. Just as we’ve been able to improve rockets, satellites and data systems over 60 years, we’ve made great improvements to spacesuits.

When the first woman and next man step foot on the Moon in 2024, they will be wearing the next generation of spacesuit, called the Exploration Extravehicular Mobility Unit, or xEMU for short. The new suit can be used under different conditions for various tasks, including walking, driving rovers or collecting samples. The design will also allow the suits to be used for spacewalks on the space station, or Gateway – our upcoming spaceship that will orbit the Moon. Future missions to Mars can build on the core suit technologies with additional upgrades for use in the Martian atmosphere and greater gravity.
60 Years of Improvements

Even before we had astronauts, pilots were using pressurized suits to fly at high speeds at altitudes where the air was too thin to breathe. Our first spacesuits – shown here worn by the first NASA astronauts in 1959 – were variations of the suit used by Navy test pilots.

The Gemini spacesuit – shown here in a photo of astronaut Ed White making the first American spacewalk in 1965 – added a line that could connect the astronaut to the spacecraft for oxygen, and which also served as a tether when they left the capsule for a spacewalk.

The Apollo astronauts had to completely separate themselves from the lunar module, so we added a portable life support unit, which the astronauts carried on their backs. The photo above shows the life support system on the suit of Apollo 11 astronaut Buzz Aldrin as he deploys lunar experiments in 1969.
Though the bulky suits weren’t exactly easy to maneuver, astronauts still managed to get their jobs done and enjoy themselves doing it.
A Great Moment in Spacesuit History: Singing on the Moon
What, you wouldn’t sing if you were on the moon?
Different Suits for Different Functions

We have used different suits for different purposes. During the Space Shuttle program, astronauts inside the shuttle wore these orange “pumpkin” suits, which were designed to be worn within the cabin.

On spacewalks, special suits – made to be worn only outside the spacecraft – provided high mobility, more flexibility and life support as the astronauts worked in zero gravity.

During construction of the International Space Station, we should have issued a hard hat and a pair of steel-toed boots with each suit. Astronauts conducted more than 200 spacewalks as part of building the station, which took place from 1998 until 2011. Above, an astronaut at the end of the shuttle’s robotic arm is maneuvered back into the shuttle’s payload bay with a failed pump during the shuttle’s final flight in 2011.
#MissionAccomplished

Spacesuits are rarely the story themselves, but they make it possible for our astronauts to get their jobs done, even when they have to improvise. In the picture above, astronauts on a 1992 space shuttle mission are conducting a spacewalk they hadn’t originally planned on. The crew was originally supposed to use a specially designed grab bar to capture the INTELSAT VI satellite. Two attempts to use the grab bar on two-person spacewalks failed, so we improvised a plan to add a third spacewalker and have all three go outside and literally grab the satellite.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
More Posts from Nasa and Others
Record Number of Americans Apply to #BeAnAstronaut

On Dec. 14, 2015, we announced that astronaut applications were open on USAJOBS. The window for applications closed on Feb. 18. We’re happy to announce that we have received more than 18,300 applications from excited individuals from around the country, all hoping to join the 2017 astronaut class. This surpasses the more than 6,100 received in 2012 for the most recent astronaut class, and the previous record - 8,000 applicants in 1978.

So you applied to be an astronaut...now what?
Since the applications closed on Feb. 18, many people are curious to know…what’s next? Let us help you navigate the selection process:

Now that we have received all the applications, we will review them to determine the “Highly Qualified” applicants. This process will take place through summer 2016.
What is a “Highly Qualified” Applicant?
The diversity of experiences is what separates the highly qualified from qualified. Experience that demonstrates good leadership, fellowship and decision making are beneficial.
Between fall 2016 and spring 2017, interviewees will be brought to Johnson Space Center for evaluation. This process will help us determine the finalists, which takes place in spring 2017.
Finally, in summer 2017, the Astronaut Candidate Class of 2017 is announced! These candidates will report to Johnson Space Center starting in August 2017.
To view the full astronaut candidate selection process timeline, visit: http://astronauts.nasa.gov/content/timeline.htm
*Note that the high volume of applications received, dates in the timeline could be adjusted.
Why do we need more astronauts?

We are continuing human spaceflight on the International Space Station, which has a continuous crew of six people on board. The Boeing and SpaceX commercial crew spacecraft that will travel to the station both have seats for four astronauts (the current Soyuz spacecraft, on which astronauts travel, only has three). This will add a seventh astronaut to the orbiting laboratory, and enable us to do more science!
How many astronauts will be selected?
The exact number will be determined by mission requirements, but current analysis shows about 8 - 14 astronauts will be needed. The final number will depend on updates to program plans, budgets, etc.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

Thanks for all of the great questions! Follow me at @Astro_Jessica on Twitter and Instagram and follow the Orion space capsule as it prepares to fly to deep space on Twitter and Facebook. Follow NASA on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

NASA Spotlight: Christina Hernandez, NASA Mars 2020 Rover Instrument Engineer
“I was in love with the beauty of space. It was my introduction to appreciating the beauty of complex, chaotic things—black holes, giant gas planets, or killer asteroids—that got my imagination riled up.“ -Christina Hernandez
Christina Hernandez, a space enthusiast and self-proclaimed nerd, is an aerospace engineer at our Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California where she works as an instrument engineer on our newest rover mission – Mars2020. The Mars2020 rover is a robotic scientist that is launching to the Red Planet next year. If you would like to launch to the Red Planet as well, you can Send Your Name to Mars along with millions of other people! Christina’s job is to make sure that the instruments we send to the Martian surface are designed, built, tested and operated correctly so we can retrieve allll the science. When she isn’t building space robots, she loves exploring new hiking trails, reading science fiction and experimenting in the kitchen. Christina took a break from building our next Martian scientist to answer some questions about her life and her career:
If you could go to Mars, would you? And what are three things you’d bring with you?
Only if I had a round trip ticket! I like the tacos and beach here on Earth too much. If I could go, I would bring a bag of Hot Cheetos, a Metallica album, and the book On the Shoulders of Giants.
If you could name the Mars2020 rover, what would you name it and why?

Pilas, a reference to a phrase my family says a lot, ponte las pilas. It literally means put your batteries on or in other words, get to work, look alive or put some energy into it. Our rover is going to need to have her batteries up and running for all the science she is going to be doing! Luckily, the rover has a radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) to help keep the batteries charged!
What’s been your most memorable day at NASA?

It’s been seeing three of the instruments I worked on getting bolted and connected to the flight rover. I’ll never forget seeing the first 1’s and 0’s being exchanged between the rover compute element (RCE), the rover’s on-board brain, and the instruments’ electronics boxes (their brains). I am sure it was a wonderful conversation between the two!
It’s a long journey to get from Earth to Mars. What would be on your ultimate road trip playlist?
Metallica, The Cure, Queen, Echo and the Bunnymen, Frank Sinatra, Ramon Ayala, AC/DC, Selena, Los Angeles Azules, ughhhh – I think I just need a Spotify subscription to Mars.
What is one piece of advice you wish someone would’ve told you?

Take your ego out of the solution space when problem solving.
Do you have any secret skills, talents, or hobbies?

I love reading. Each year I read a minimum of 20 books, with my goal this year being 30 books. It’s funny I increased my goal during what has definitely been my busiest year at work. I recently got into watercolor painting. After spending so much time connected at work, I started looking for more analog hobbies. I am a terrible painter right now, but I painted my first painting the other day. It was of two nebulas! It’s not too bad! I am hoping watercolor can help connect me more to the color complexities of nature...and it’s fun!
What’s a project or problem that you would love the ability to tackle/work on?
I would love to work on designs for planetary human explorers. So far, I have focused on robotic explore, but when you throw a “loveable, warm, squishy thing” into the loop, its creates a different dimension to design – both with respect to operability and risk.
Thanks so much Christina! The Mars2020 rover is planned to launch on July 17, 2020, and touch down in Jezero crater on Mars on February 18, 2021.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com

What are Perseid Meteors, and why should you be excited for them this year? Let us tell you!
The Perseid meteor shower is caused by debris from Comet Swift-Tuttle as it swings through the inner solar system and ejects a trail of dust and gravel along its orbit. When the Earth passes through the debris, specs of comet-stuff hit the atmosphere at 140,000 mph and disintegrate in flashes of light. Meteors from this comet are called Perseids because they seem to fly out of the constellation Perseus.

Last year, this meteor shower peaked during a bright “supermoon”, so visibility was reduced. Luckily, forecasters say the show could be especially awesome this year because the Moon is nearly new when the shower peaks on Aug. 12-13.
The best place to view the event is away from city lights around midnight. Under a clear, dark sky forecasters predict meteor rates as high as 100 per hour on peak night. So, get outside, look up and enjoy the show!
If your area has poor visibility on the peak night, we’ve got you covered! We’ll be hosting a live broadcast about the meteor shower from 10 p.m. EDT Wednesday, Aug. 12, to 2 a.m. Thursday, Aug. 13. In addition to footage from our live skycam, the program will highlight the science behind the Perseids, as well as our research related to meteors and comets. Tune in on NASA TV or our UStream Channel.
Ion Propulsion…What Is It?
Ion thrusters are being designed for a wide variety of missions – from keeping communications satellites in the proper position to propelling spacecraft throughout our solar system. But, what exactly is ion propulsion and how does an ion thruster work? Great question! Let’s take a look:

Regular rocket engines: You take a gas and you heat it up, or put it under pressure, and you push it out of the rocket nozzle, and the action of the gas going out of the nozzle causes a reaction that pushes the spacecraft in the other direction.
Ion engines: Instead of heating the gas up or putting it under pressure, we give the gas xenon a little electric charge, then they’re called ions, and we use a big voltage to accelerate the xenon ions through this metal grid and we shoot them out of the engine at up to 90,000 miles per hour.

Something interesting about ion engines is that it pushes on the spacecraft as hard as a single piece of paper pushes on your hand while holding it. In the zero gravity, frictionless, environment of space, gradually the effect of this thrust builds up. Our Dawn spacecraft uses ion engines, and is the first spacecraft to orbit two objects in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
To give you a better idea, at full throttle, it would take our Dawn spacecraft four days to accelerate from zero to sixty miles per hour. That may sounds VERY slow, but instead of thrusting for four days, if we thrust for a week or a year as Dawn already has for almost five years, you can build up fantastically high velocity.

Why use ion engines? This type of propulsion give us the maneuverability to go into orbit and after we’ve been there for awhile, we can leave orbit and go on to another destination and do the same thing.
As the commercial applications for electric propulsion grow because of its ability to extend the operational life of satellites and to reduce launch and operation costs, we are involved in work on two different ion thrusters of the future: the NASA Evolutionary Xenon Thruster (NEXT) and the Annular Engine. These new engines will help reduce mission cost and trip time, while also traveling at higher power levels.
Learn more about ion propulsion HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
From an astronauts perspective, what is your opinion on movies like Interstellar and Gravity?
Solar System: Things to Know This Week
Our solar system is huge, let us break it down for you. Here are a few things to know this week:
1. Juno Eyes on Jupiter

After a journey of more than five years, the Juno spacecraft is ready for its detailed look at Jupiter—arrival date: July 4. Using Eyes on the Solar System and data from the Juno flight team, you can take a virtual ride onboard the spacecraft in the "Eyes on Juno" simulation.
2. Taking a Spacecraft for a Spin

Preparations for the launch of the OSIRIS-REx asteroid mission are spinning up, literally. Here, the spacecraft can be seen rotating on a spin table during a weight and center of gravity verification test at our Kennedy Space Center. Liftoff is scheduled for Sept. 8. This spacecraft will travel to a near-Earth asteroid called Bennu and bring a small sample back to Earth for study.
3. Long-Range (Or at Least Long-Distance) Weather Report
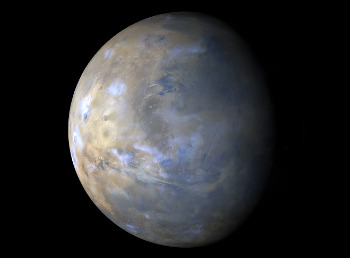
Our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter acquires a global view of the red planet and its weather every day. Last week, dust storms continued along the south polar ice cap edge. Northern portions of Sirenum, Solis, and Noachis also experienced some local dust-lifting activity. A large dust storm propagated eastward over the plains of Arcadia at the beginning of the week, but subsided just a few days later over Acidalia.
4. Hello from the Dark Side

The New Horizons spacecraft took this stunning image of Pluto only a few minutes after closest approach in July 2015, with the sun on the other side of Pluto. Sunlight filters through Pluto's complex atmospheric haze layers. Looking back at Pluto with images like this gives New Horizons scientists information about Pluto's hazes and surface properties that they can't get from images taken on approach.
5. A Titanic Encounter

On June 7, our Cassini orbiter will fly very close by Saturn's giant, haze-shrouded moon Titan. Among the targets of its observations will be the edge of the vortex that swirls in Titan's thick atmosphere near its south pole.
Want to learn more? Read our full list of the 10 things to know this week about the solar system HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Take a deep breath. Even if the air looks clear, it is nearly certain that you will inhale millions of solid particles and liquid droplets. These ubiquitous specks of matter are known as aerosols, and they can be found in the air over oceans, deserts, mountains, forests, ice, and every ecosystem in between.
If you have ever watched smoke billowing from a wildfire, ash erupting from a volcano, or dust blowing in the wind, you have seen aerosols. Satellites like Terra, Aqua, Aura, and Suomi NPP “see” them as well, though they offer a completely different perspective from hundreds of kilometers above Earth’s surface. A version of one of our models called the Goddard Earth Observing System Forward Processing (GEOS FP) offers a similarly expansive view of the mishmash of particles that dance and swirl through the atmosphere.
The visualization above highlights GEOS FP model output for aerosols on August 23, 2018. On that day, huge plumes of smoke drifted over North America and Africa, three different tropical cyclones churned in the Pacific Ocean, and large clouds of dust blew over deserts in Africa and Asia. The storms are visible within giant swirls of sea salt aerosol(blue), which winds loft into the air as part of sea spray. Black carbon particles (red) are among the particles emitted by fires; vehicle and factory emissions are another common source. Particles the model classified as dust are shown in purple. The visualization includes a layer of night light data collected by the day-night band of the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) on Suomi NPP that shows the locations of towns and cities.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
Travel to Exotic Destinations in our Galaxy!
The planets beyond our solar system – exoplanets – are so far away, often trillions of miles, that we don’t have the technology to truly see them. Even the best photos show the planets as little more than bright dots. We’ve confirmed more than 5,000 exoplanets, but we think there are billions. Space telescopes like Hubble aren’t able to take photos of these far-off worlds, but by studying them in different wavelengths of light (colors), we’ve learned enough about conditions on these planets that we can illustrate them.

We know, thanks to the now-retired Spitzer Space Telescope, that there is a thick atmosphere on a planet called 55 Cancri e about 40 light-years away. And Hubble found silicate vapor in the atmosphere of this rocky world. We also know it’s scorching-close to its Sun-like star, so … lava. Lots and lots of lava. This planet is just one of the many that the James Webb Space Telescope will soon study, telling us even more about the lava world!
You can take a guided tour of this planet (and others) and see 360-degree simulations at our new Exoplanet Travel Bureau.
Travel to the most exotic destinations in our galaxy, including:
Kepler-16b, a planet with two suns.

Then there’s PSO J318.5-22, a world with no sun that wanders the galaxy alone. The nightlife would never end on a planet without a star.

TRAPPIST-1e, which will also be studied by the Webb Space Telescope, is one of seven Earth-sized planets orbiting a star about 40 light-years from Earth. It’s close enough that, if you were standing on this exoplanet, you could see our Sun as a star in the Leo constellation! You can also see it on the poster below: look for a yellow star to the right of the top person’s eye.

We haven’t found life beyond Earth (yet) but we’re looking. Meanwhile, we can imagine the possibility of red grass and other plants on Kepler-186f, a planet orbiting a red dwarf star.

We can also imagine what it might be like to skydive on a super-Earth about seven times more massive than our home planet. You would fall about 35% faster on a super-Earth like HD 40307g, making for a thrilling ride!

Any traveler is going to want to pick up souvenirs, and we have you covered. You can find free downloads of all the posters here and others! What are you waiting for? Come explore with us!

Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!
Image credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech

Check out tiny-house-looking satellite Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich
It might look like something you’d find on Earth, but this piece of technology has a serious job to do: track global sea level rise with unprecedented accuracy. It’s #SeeingTheSeas mission will:
Provide information that will help researchers understand how climate change is reshaping Earth's coastlines – and how fast this is happenin.
Help researchers better understand how Earth's climate is changing by expanding the global atmospheric temperature data record
Help to improve weather forecasts by providing meteorologists information on atmospheric temperature and humidity.
Tune in tomorrow, Nov. 21 at 11:45 a.m. EST to watch this U.S.-European satellite launch to space! Liftoff is targeted for 12:17 p.m. EST. Watch HERE.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com.
-
 mahmutagac liked this · 3 years ago
mahmutagac liked this · 3 years ago -
 wondering4eversblog liked this · 4 years ago
wondering4eversblog liked this · 4 years ago -
 sulestarlight liked this · 4 years ago
sulestarlight liked this · 4 years ago -
 funkedup reblogged this · 4 years ago
funkedup reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 funkedup liked this · 4 years ago
funkedup liked this · 4 years ago -
 nunyo-bizznez liked this · 4 years ago
nunyo-bizznez liked this · 4 years ago -
 apriiae liked this · 4 years ago
apriiae liked this · 4 years ago -
 archive099 liked this · 4 years ago
archive099 liked this · 4 years ago -
 chimgadad liked this · 4 years ago
chimgadad liked this · 4 years ago -
 spaceouija reblogged this · 4 years ago
spaceouija reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 finnnsworld liked this · 4 years ago
finnnsworld liked this · 4 years ago -
 alienlamp reblogged this · 4 years ago
alienlamp reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 alienlamp liked this · 4 years ago
alienlamp liked this · 4 years ago -
 sleepygrumpylumpy reblogged this · 5 years ago
sleepygrumpylumpy reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fandomforever369 liked this · 5 years ago
fandomforever369 liked this · 5 years ago -
 karchuckles liked this · 5 years ago
karchuckles liked this · 5 years ago -
 purplerabbit-things liked this · 5 years ago
purplerabbit-things liked this · 5 years ago -
 rougeaubebeaute reblogged this · 5 years ago
rougeaubebeaute reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lee-lee-la liked this · 5 years ago
lee-lee-la liked this · 5 years ago -
 gorjuicylicious reblogged this · 5 years ago
gorjuicylicious reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 gorjuicylicious liked this · 5 years ago
gorjuicylicious liked this · 5 years ago -
 samsredemption liked this · 5 years ago
samsredemption liked this · 5 years ago -
 theoneandonlybastard liked this · 5 years ago
theoneandonlybastard liked this · 5 years ago -
 unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago
unknown-uwoit liked this · 5 years ago -
 panoramabyk liked this · 5 years ago
panoramabyk liked this · 5 years ago -
 attonitusnaturae reblogged this · 5 years ago
attonitusnaturae reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 ioannae-d-arc liked this · 5 years ago
ioannae-d-arc liked this · 5 years ago -
 r-hct liked this · 5 years ago
r-hct liked this · 5 years ago -
 rougeaubebeaute liked this · 5 years ago
rougeaubebeaute liked this · 5 years ago -
 justkillmealreadym8 liked this · 5 years ago
justkillmealreadym8 liked this · 5 years ago -
 wolvesandwerewolvesbaby reblogged this · 5 years ago
wolvesandwerewolvesbaby reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 colettedelaurel liked this · 5 years ago
colettedelaurel liked this · 5 years ago -
 zephyr-of-the-south liked this · 5 years ago
zephyr-of-the-south liked this · 5 years ago -
 exorcise-me-daddy liked this · 5 years ago
exorcise-me-daddy liked this · 5 years ago -
 themidnightgoosepal liked this · 5 years ago
themidnightgoosepal liked this · 5 years ago -
 aestesianobilis reblogged this · 5 years ago
aestesianobilis reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 lovinthemelanin liked this · 5 years ago
lovinthemelanin liked this · 5 years ago -
 aaaavgs liked this · 5 years ago
aaaavgs liked this · 5 years ago -
 adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago
adt-space reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 5 years ago
pinkiepieaddict reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 santoshkumardwivedi liked this · 5 years ago
santoshkumardwivedi liked this · 5 years ago
Explore the universe and discover our home planet with the official NASA Tumblr account
1K posts