What Happened To Mars?
What Happened to Mars?
Billions of years ago, Mars was a very different world. Liquid water flowed in long rivers that emptied into lakes and shallow seas. A thick atmosphere blanketed the planet and kept it warm.

Today, Mars is bitter cold. The Red Planet’s thin and wispy atmosphere provides scant cover for the surface below.

Our MAVEN Mission
The Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission is part of our Mars Scout program. This spacecraft launched in November 2013, and is exploring the Red Planet’s upper atmosphere, ionosphere and interactions with the sun and solar wind.

The purpose of the MAVEN mission is to determine the state of the upper atmosphere of Mars, the processes that control it and the overall atmospheric loss that is currently occurring. Specifically, MAVEN is exploring the processes through which the top of the Martian atmosphere can be lost to space. Scientists think that this loss could be important in explaining the changes in the climate of Mars that have occurred over the last four billion years.
New Findings
Today, Nov. 5, we will share new details of key science findings from our ongoing exploration of Mars during a news briefing at 2 p.m. EDT. This event will be broadcast live on NASA Television. Have questions? Use #askNASA during the briefing.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
More Posts from Intergalacticnerd and Others

NASA just released the most detailed photo of space ever taken
The picture of the Andromeda galaxy, the nearest spiral galaxy to our own, is comprised of a mind-boggling 1.5 billion pixels and was snapped from 2.5 million light years away by the powerful Hubble Space Telescope.
See it in all its glory

The Shakespearean Moons of Uranus
This weekend marks the 400th anniversary of Shakespeare’s death, and we’re highlighting the moons of Uranus; some of which are named after characters from his works.

While most of the moons orbiting other planets take their names from Greek mythology, Uranus’ moons are unique in bing named for Shakespearean characters, along with a couple of them being named for characters from the works of Alexander Pope.

Using the Hubble Space Telescope and improved ground-based telescopes, astronomers have discovered a total of 27 known moons around Uranus.
Here’s a sampling of some of the unique aspects of the moons:
Miranda

Shakespearean work: The Tempest
Miranda, the innermost and smallest of the five major satellites, has a surface unlike any other moon that’s been seen. It has a giant fault canyon as much as 12 times as deep as the Grand Canyon, terraced layers and surfaces that appear very old, and others that look much younger.
Ariel

Shakespearean work: The Tempest
Ariel has the brightest and possibly the youngest surface among all the moons of Uranus. It has a few large craters and many small ones, indicating that fairly recent low-impact collisions wiped out the large craters that would have been left by much earlier, bigger strikes. Intersecting valleys pitted with craters scars its surface.
Oberon

Shakespearean work: A Midsummer Night’s Dream
Oberon, the outermost of the five major moons, is old, heavily cratered and shows little signs of internal activity. Unidentified dark material appears on the floors of many of its craters.
Cordelia and Ophelia

Shakespearean works: Cordelia - King Lear; Ophelia - Hamlet
Cordelia and Ophelia are shepherd moons that keep Uranus’ thin, outermost “epsilon” ring well defined.
Between them and miranda is a swarm of eight small satellites unlike any other system of planetary moons. This region is so crowded that astronomers don’t yet understand how the little moons have managed to avoid crashing into each other. They may be shepherds for the planet’s 10 narrow rings, and scientists think there must be still more moons, interior to any known, to confine the edges of the inner rings.
Want to learn more about all of Uranus’s moons? Visit: http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/uranus/moons
Check out THIS blog from our Chief Scientist Ellen Stofan, where she reflects on the life and legacy of William Shakespeare on the 400th anniversary of his death on April 23, 1616.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space: http://nasa.tumblr.com
Dust, stars, and cosmic rays swirling around Comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, captured by the Rosetta probe. (Source)


NGC 660. A rare galaxy type, polar ring galaxies have a substantial population of stars, gas, and dust orbiting in rings nearly perpendicular to the plane of a flat galactic disk. Only about a dozen of such galaxies have been discovered
Source: https://imgur.com/z73B8o3


NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day 2016 January 27
An Airglow Fan from Lake to Sky
Why would the sky look like a giant fan? Airglow. The featured intermittent green glow appeared to rise from a lake through the arch of our Milky Way Galaxy, as captured last summer next to Bryce Canyon in Utah, USA. The unusual pattern was created by atmospheric gravity waves, ripples of alternating air pressure that can grow with height as the air thins, in this case about 90 kilometers up. Unlike auroras powered by collisions with energetic charged particles and seen at high latitudes, airglow is due to chemiluminescence, the production of light in a chemical reaction. More typically seen near the horizon, airglow keeps the night sky from ever being completely dark.

Black Holes are not so Black (Part 3) - Gravitational Waves
The existence of Gravitational Waves have been confirmed. But you probably have heard that. In this post, we will break down this profound discovery into comprehend-able chunks.
This is going to be a amazing journey. Ready ?
Redefining Gravity
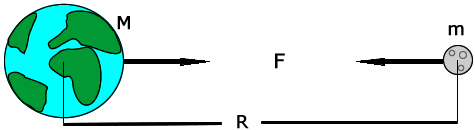
When we usually talk of Gravitation we are bound to think like Newton, where objects are assumed to exerting a force upon each other.
Like imaginary arrows of force in space. But this picture, although good for high school crumbled, with the advent of Einstein’s theory of Relativity.
What is the Space-Time Fabric?
Think of space-time fabric as an actual cloth of fabric. ( An analogy )

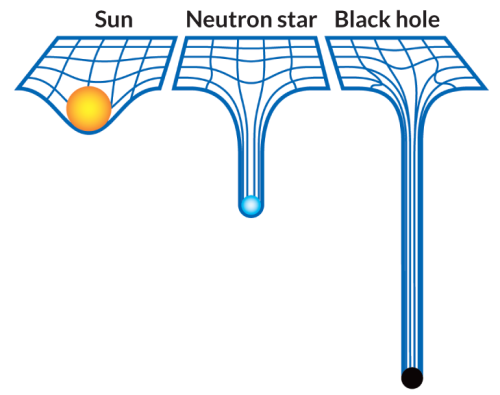
When you place an object on the fabric, the cloth curves. This is exactly what happens in the solar system as well.

The sun with such a huge mass bends the space-time fabric. And the earth and all the planets are kept in orbit by following this curvature that has been made by the sun.
Attributing to the various masses of objects, the way they bend this fabric also varies.
What are Gravitational Waves?
If you drop an object in a medium such as water, they produce ripples that propagate as waves through the medium.

Similarly, Gravitational waves are ripples in space-time fabric produced when you drag heavy objects through space time.
And the nature of these waves is that they don’t require a medium to propagate.
How do you make one?
Everything with mass/energy can create these waves.

Source
Two persons dancing around each other in space too can create gravitational waves. But the waves would be extremely faint.
You need something big and massive accelerating through space-time in order to even detect them.

And orbiting binary stars/black holes are valuable in this retrospect.
How can you detect them?
Let’s turn to the problem to detecting them assuming you do find binary stars/black-holes in the wondrous space to suite your needs.
Well, for starters you cannot use rocks/ rulers to measure them because as the space expands and contracts, so do the rocks. ( the distances will remain same in both the cases )

Here’s where the high school fact that the speed of Light is a constant no matter what plays an important and pivotal role.
If the space expands, the time taken for light to reach from A to B would be longer. And if it contracts, the time taken for it to reach from A to B would be smaller.

PC: PHDComics
By allowing the light waves from the contraction and expansion to interfere with each other, such as done in any interferometry experiment we can detect the expansion or contraction. Voila!
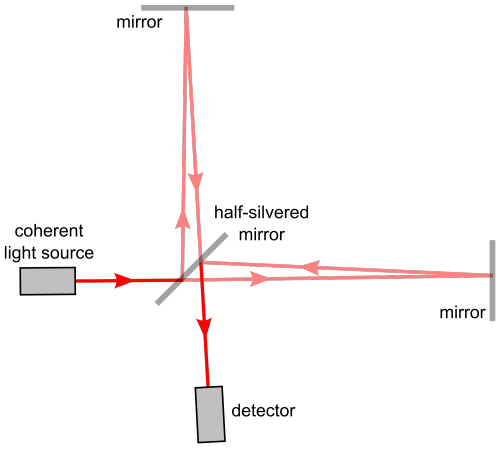
And this is exactly what they did! ( on a macroscopic level ) at LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory)
14 September 2015

Two Black Holes with masses of 29 and 36 solar masses merged together some 1.3 Billion light years away.
Two Black Holes colliding is the header animation of the ‘Black Holes are not so Black Series’, in case if you haven’t noticed.

The merger of these two black holes results in the emission of energy equivalent to 3 solar masses as Gravitational Waves.
This signal was seen by both LIGO detectors, in Livingston and Hanford, with a time difference of 7 milliseconds.
And with the measurement of this time difference, physicists have pronounced the existence of Gravitational Waves.

Source
All this is most certainly easily said than done and requires meticulous and extensive research, not to mention highly sensitive instruments.
Had they not have measured this time difference, we might have had to wait for the merger for more massive black holes to collide and maybe even build more sensitive instruments to detect these waves.
And Einstein predicted this a 100 years back!

Mind Blown!
Note: Hope you are able to understand and appreciate the profundity of the discovery done by mankind.
** All animations used here are merely for Educational purposes. If you have any issues, please write to us at : [email protected]

Astronaut Leland Melvin includes his rescued dogs in best NASA portrait ever.










A recap of January in pictures! Winters the best time for astrophotography which is why I’ve had plenty of opportunities to get outside and capture the cosmos!
-
 ohturtlesmyturtles liked this · 3 years ago
ohturtlesmyturtles liked this · 3 years ago -
 noorhb reblogged this · 4 years ago
noorhb reblogged this · 4 years ago -
 miraculousgoldenarmy liked this · 5 years ago
miraculousgoldenarmy liked this · 5 years ago -
 goneau2xr reblogged this · 5 years ago
goneau2xr reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 xnzda reblogged this · 5 years ago
xnzda reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 astro-science-math reblogged this · 5 years ago
astro-science-math reblogged this · 5 years ago -
 fanoftoday liked this · 6 years ago
fanoftoday liked this · 6 years ago -
 ohmygrath liked this · 6 years ago
ohmygrath liked this · 6 years ago -
 manic-no liked this · 6 years ago
manic-no liked this · 6 years ago -
 gakittajp liked this · 6 years ago
gakittajp liked this · 6 years ago -
 kherchach-blog liked this · 6 years ago
kherchach-blog liked this · 6 years ago -
 pinkpanthress liked this · 6 years ago
pinkpanthress liked this · 6 years ago -
 praecavere-dracones reblogged this · 6 years ago
praecavere-dracones reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 queencfthestars liked this · 6 years ago
queencfthestars liked this · 6 years ago -
 at-the-centre-of-it-all reblogged this · 6 years ago
at-the-centre-of-it-all reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 esztikeh15 liked this · 6 years ago
esztikeh15 liked this · 6 years ago -
 soft-sunshine-n-flowers reblogged this · 6 years ago
soft-sunshine-n-flowers reblogged this · 6 years ago -
 soft-sunshine-n-flowers liked this · 6 years ago
soft-sunshine-n-flowers liked this · 6 years ago -
 themintjelly liked this · 6 years ago
themintjelly liked this · 6 years ago -
 ninjamonster97 liked this · 6 years ago
ninjamonster97 liked this · 6 years ago -
 mattdvm liked this · 6 years ago
mattdvm liked this · 6 years ago -
 bunkerblitz liked this · 7 years ago
bunkerblitz liked this · 7 years ago -
 flydaygryphontown reblogged this · 7 years ago
flydaygryphontown reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 sorentheowl liked this · 7 years ago
sorentheowl liked this · 7 years ago -
 havesomepurplepoison liked this · 7 years ago
havesomepurplepoison liked this · 7 years ago -
 w0wls reblogged this · 7 years ago
w0wls reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 w0wls liked this · 7 years ago
w0wls liked this · 7 years ago -
 wasted-life-musings liked this · 7 years ago
wasted-life-musings liked this · 7 years ago -
 fandomitor reblogged this · 7 years ago
fandomitor reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 fandomitor liked this · 7 years ago
fandomitor liked this · 7 years ago -
 selfish-giant liked this · 7 years ago
selfish-giant liked this · 7 years ago -
 506k liked this · 7 years ago
506k liked this · 7 years ago -
 universumnow reblogged this · 7 years ago
universumnow reblogged this · 7 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago
astrotidbits-blog liked this · 8 years ago -
 firstesource-com liked this · 8 years ago
firstesource-com liked this · 8 years ago -
 lunaticsoup liked this · 8 years ago
lunaticsoup liked this · 8 years ago -
 nonflamminghomo-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago
nonflamminghomo-blog reblogged this · 8 years ago -
 nonflamminghomo-blog liked this · 8 years ago
nonflamminghomo-blog liked this · 8 years ago
"Astronomy compels the soul to look upwards and leads us from this world to another." - Plato
147 posts